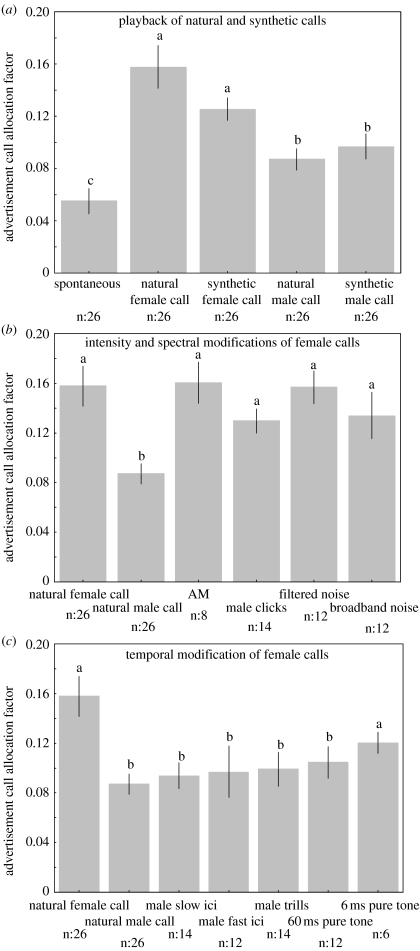
Figure 3.
Results of playbacks of non-modified calls and modified female calls on male Xenopus laevis advertisement call allocation factors (mean±s.e.m). (a) Spontaneous calling compared with the response to natural female rapping call, synthetic female call, natural male advertisement call and synthetic male call. (b) Response to intensity modification (AM) and frequency modifications (male clicks, filtered noise, broadband noise) of female calls compared with natural controls. (c) Response to temporal modifications (male slow ICI, male fast ICI, male trills, 60 ms pure tone, 6 ms pure tone) of female calls compared with natural controls. Comparisons between responses to different stimuli were performed using a one-way ANOVA (F(13,220)=6.129, p<10−5), followed by t-test and Dunnett post hoc test with Bonferroni correction. Means represented with different letters are significantly different (p<0.05). Sample sizes are indicated for each stimulus.