Abstract
Juvenile onset spondyloarthropathy (SpA) is a term that refers to a group of human leucocyte antigen (HLA)-B27 associated inflammatory disorders affecting children under the age of 16 years, producing a continuum of clinical symptoms through adulthood. This disease is characterised by enthesopathy and arthropathy affecting the joints of the lower extremities and seronegativity for IgM rheumatoid factor and antinuclear antibodies. Children usually present with undifferentiated SpA and progress to differentiated forms over time. Except for the prevalence of some clinical features at onset, the pathogenic and clinical aspects of juvenile onset SpAs resemble those of the adult disease. Thus application of the same or similar therapeutic measures for both juvenile and adult onset SpAs seems logical. Current treatments for juvenile onset SpA provide symptomatic improvement, but do not alter disease progression. The increased expression of tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) in synovial tissue of patients with adult and juvenile onset SpA and its correlation with infiltration of inflammatory mediators into the synovia suggest a significant pathogenic role of this cytokine. Clinical trials of anti-TNFα antibody (infliximab) therapy in patients with adult onset SpA have demonstrated significant clinical improvement in inflammatory pain, function, disease activity, and quality of life in correlation with histological and immunohistochemical evidence of modulation of synovial inflammatory processes. These promising findings suggest that anti-TNFα therapy may confer similar benefits in patients with juvenile onset SpA.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (190.5 KB).
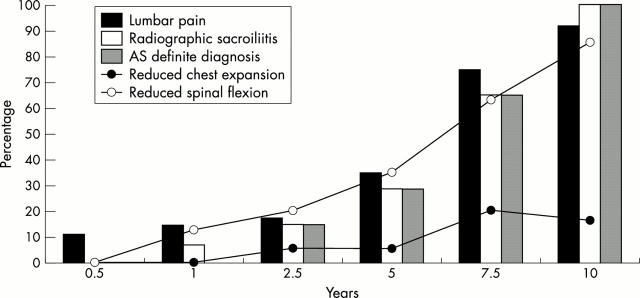
Figure 1 .
Progression of children with juvenile onset undifferentiated spondyloarthropathy to fulfilment of the modified New York diagnostic criteria for AS over a 10 year period. The percentages of patients fulfilling each criterion are shown for each time. Most patients fulfil diagnostic criteria for definite AS after a mean of 7.5 years (range 5–10) after the onset of symptoms of juvenile onset SpA. Reproduced with permission of the authors and Rheumatic Disease Clinics of North America from Burgos-Vargas R et al. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 1997;23:569–98. Copyright © 1997 W B Saunders Company.
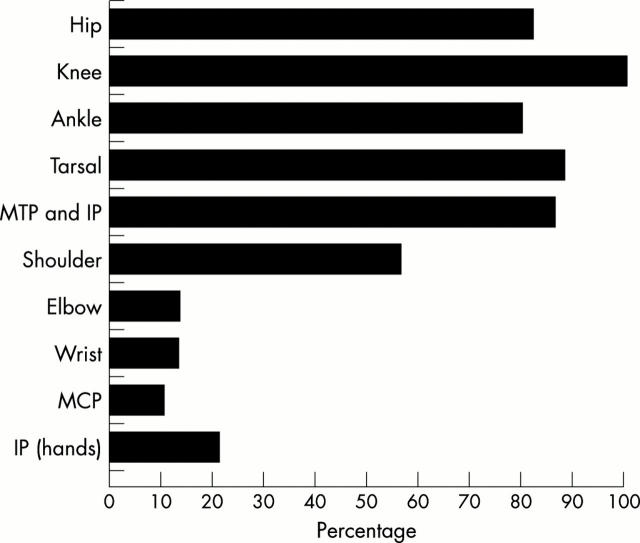
Figure 2 .
Cumulative frequency of joint disease in juvenile onset ankylosing spondylitis 10 years after diagnosis. Reproduced with permission of the authors and Rheumatic Disease Clinics of North America from Burgos-Vargas R et al. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 1997;23:569–98. Copyright © 1997 W B Saunders Company.
Figure 3 .

Long term structural changes of the feet in a 20 year old patient with juvenile onset AS. (A) Dorsoplantar aspect showing metatarsophalangeal joint surface erosions and misalignment. (B) Left foot oblique view showing ankylosis of the first metatarsal and cuneal bones, metatarsophalangeal joint subluxations and enthesophytes at the margin of the 5th metatarsal-cuneal joint. (C, D) Right and left lateral views showing a spectrum of changes, including enthesophytosis at the plantar fascia attachment to the calcaneus and complete fusion of the tarsal bones (ankylosing tarsitis in C and enthesophytosis of the talonavicular joint in D). These previously unpublished figures are provided courtesy of Dr R Burgos-Vargas.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson Gäre B. Juvenile arthritis--who gets it, where and when? A review of current data on incidence and prevalence. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1999 May-Jun;17(3):367–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeten D., Kruithof E., Van den Bosch F., Demetter P., Van Damme N., Cuvelier C., De Vos M., Mielants H., Veys E. M., De Keyser F. Immunomodulatory effects of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy on synovium in spondylarthropathy: histologic findings in eight patients from an open-label pilot study. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Jan;44(1):186–195. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200101)44:1<186::AID-ANR25>3.0.CO;2-B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barabino A., Gattorno M., Cabria M., Sormani M. P., Occhi M., Villavecchia G., Gandullia P., Buoncompagni A., Castellano E., Picco P. 99mTc-white cell scanning to detect gut inflammation in children with inflammatory bowel diseases or spondyloarthropathies. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1998 May-Jun;16(3):327–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowyer S., Roettcher P. Pediatric rheumatology clinic populations in the United States: results of a 3 year survey. Pediatric Rheumatology Database Research Group. J Rheumatol. 1996 Nov;23(11):1968–1974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer G. S., Lanier A. P., Templin D. W. Prevalence rates of spondyloarthropathies, rheumatoid arthritis, and other rheumatic disorders in an Alaskan Inupiat Eskimo population. J Rheumatol. 1988 Apr;15(4):678–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Bollow M., Neure L., Seipelt E., Seyrekbasan F., Herbst H., Eggens U., Distler A., Sieper J. Use of immunohistologic and in situ hybridization techniques in the examination of sacroiliac joint biopsy specimens from patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Apr;38(4):499–505. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Brandt J., Listing J., Zink A., Alten R., Golder W., Gromnica-Ihle E., Kellner H., Krause A., Schneider M. Treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis with infliximab: a randomised controlled multicentre trial. Lancet. 2002 Apr 6;359(9313):1187–1193. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(02)08215-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Laitko S., Treharne J., Eggens U., Wu P., Distler A., Sieper J. Chlamydia pneumoniae--a new causative agent of reactive arthritis and undifferentiated oligoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1994 Feb;53(2):100–105. doi: 10.1136/ard.53.2.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Xiang J., Brandt J., Maetzel H., Haibel H., Wu P., Kohler S., Rudwaleit M., Siegert S., Radbruch A. Treatment of spondyloarthropathies with antibodies against tumour necrosis factor alpha: first clinical and laboratory experiences. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000 Nov;59 (Suppl 1):i85–i89. doi: 10.1136/ard.59.suppl_1.i85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M., Wordsworth P. Genotyping HLA-B27 in spondyloarthropathies. J Rheumatol. 1998 Apr;25(4):820–821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgos-Vargas R., Clark P. Axial involvement in the seronegative enthesopathy and arthropathy syndrome and its progression to ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol. 1989 Feb;16(2):192–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgos-Vargas R., Pacheco-Tena C., Vázquez-Mellado J. Juvenile-onset spondyloarthropathies. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1997 Aug;23(3):569–598. doi: 10.1016/s0889-857x(05)70348-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgos-Vargas R. Spondyloarthropathies and psoriatic arthritis in children. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1993 Sep;5(5):634–643. doi: 10.1097/00002281-199305050-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgos-Vargas R., Vázquez-Mellado J. The early clinical recognition of juvenile-onset ankylosing spondylitis and its differentiation from juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Jun;38(6):835–844. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabral D. A., Malleson P. N., Petty R. E. Spondyloarthropathies of childhood. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1995 Oct;42(5):1051–1070. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)40053-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabral D. A., Oen K. G., Petty R. E. SEA syndrome revisited: a longterm followup of children with a syndrome of seronegative enthesopathy and arthropathy. J Rheumatol. 1992 Aug;19(8):1282–1285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabral D. A., Oen K. G., Petty R. E. SEA syndrome revisited: a longterm followup of children with a syndrome of seronegative enthesopathy and arthropathy. J Rheumatol. 1992 Aug;19(8):1282–1285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calin A., Elswood J. The natural history of juvenile-onset ankylosing spondylitis: a 24-year retrospective case-control study. Br J Rheumatol. 1988 Apr;27(2):91–93. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/27.2.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chikanza I. C., Kuis W., Heijnen C. J. The influence of the hormonal system on pediatric rheumatic diseases. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2000 Nov;26(4):911–925. doi: 10.1016/s0889-857x(05)70176-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuttica R. J., Scheines E. J., Garay S. M., Romanelli M. C., Maldonado Cocco J. A. Juvenile onset Reiter's syndrome. A retrospective study of 26 patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1992 May-Jun;10(3):285–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denardo B. A., Tucker L. B., Miller L. C., Szer I. S., Schaller J. G. Demography of a regional pediatric rheumatology patient population. Affiliated Children's Arthritis Centers of New England. J Rheumatol. 1994 Aug;21(8):1553–1561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink C. W. Proposal for the development of classification criteria for idiopathic arthritides of childhood. J Rheumatol. 1995 Aug;22(8):1566–1569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatø B., Aasland A., Vinje O., Førre O. Outcome and predictive factors in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile spondyloarthropathy. J Rheumatol. 1998 Feb;25(2):366–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Morteo O., Maldonado-Cocco J. A., Suárez-Almazor M. E., Garay E. Ankylosing spondylitis of juvenile onset: comparison with adult onset disease. Scand J Rheumatol. 1983;12(3):246–248. doi: 10.3109/03009748309098542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K., Jalkanen S., Lindberg A. A., Mäki-Ikola O., von Essen R., Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Isomäki H., Saario R., Arnold W. J., Toivanen A. Salmonella lipopolysaccharide in synovial cells from patients with reactive arthritis. Lancet. 1990 Mar 24;335(8691):685–688. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90804-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K., Jalkanen S., Toivanen P., Koski J., Lindberg A. A. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide in synovial fluid cells in Shigella triggered reactive arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1992 Mar;19(3):500–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratacós J., Collado A., Filella X., Sanmartí R., Cañete J., Llena J., Molina R., Ballesta A., Muñoz-Gómez J. Serum cytokines (IL-6, TNF-alpha, IL-1 beta and IFN-gamma) in ankylosing spondylitis: a close correlation between serum IL-6 and disease activity and severity. Br J Rheumatol. 1994 Oct;33(10):927–931. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/33.10.927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grom A. A., Murray K. J., Luyrink L., Emery H., Passo M. H., Glass D. N., Bowlin T., Edwards C., 3rd Patterns of expression of tumor necrosis factor alpha, tumor necrosis factor beta, and their receptors in synovia of patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Oct;39(10):1703–1710. doi: 10.1002/art.1780391013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton M. L., Gladman D. D., Shore A., Laxer R. M., Silverman E. D. Juvenile psoriatic arthritis and HLA antigens. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990 Sep;49(9):694–697. doi: 10.1136/ard.49.9.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussein A. Das Spektrum der postenteritischen reaktiven Arthritiden im Kindesalter. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd. 1987 Feb;135(2):93–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs J. C., Berdon W. E., Johnston A. D. HLA-B27-associated spondyloarthritis and enthesopathy in childhood: clinical, pathologic, and radiographic observations in 58 patients. J Pediatr. 1982 Apr;100(4):521–528. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80746-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Job-Deslandre C., Menkès C. J. Traitement des spondyloarthropathies juvéniles par la sulfasalazine. Rev Rhum Ed Fr. 1993 Jul-Sep;60(7-8):489–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanakoudi-Tsakalidou F., Pardalos G., Pratsidou-Gertsi P., Kansouzidou-Kanakoudi A., Tsangaropoulou-Stinga H. Persistent or severe course of reactive arthritis following Salmonella enteritidis infection. A prospective study of 9 cases. Scand J Rheumatol. 1998;27(6):431–434. doi: 10.1080/030097498442253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapasi K., Inman R. D. HLA-B27 expression modulates gram-negative bacterial invasion into transfected L cells. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 1;148(11):3554–3559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapasi K., Inman R. D. ME1 epitope of HLA-B27 confers class I-mediated modulation of gram-negative bacterial invasion. J Immunol. 1994 Jul 15;153(2):833–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavanaugh A. F. Anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha monoclonal antibody therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1998 Aug;24(3):593–614. doi: 10.1016/s0889-857x(05)70028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. A. Update: the twenty subtypes of HLA-B27. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2000 Jul;12(4):235–238. doi: 10.1097/00002281-200007000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruithof E., Van den Bosch F., Baeten D., Herssens A., De Keyser F., Mielants H., Veys E. M. Repeated infusions of infliximab, a chimeric anti-TNFalpha monoclonal antibody, in patients with active spondyloarthropathy: one year follow up. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002 Mar;61(3):207–212. doi: 10.1136/ard.61.3.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahesmaa R., Skurnik M., Vaara M., Leirisalo-Repo M., Nissilä M., Granfors K., Toivanen P. Molecular mimickry between HLA B27 and Yersinia, Salmonella, Shigella and Klebsiella within the same region of HLA alpha 1-helix. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Dec;86(3):399–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb02944.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lionetti P., Pupi A., Veltroni M., Fonda C., Cavicchi M. C., Azzari C., Falcini F. Evidence of subclinical intestinal inflammation by 99m technetium leukocyte scintigraphy in patients with HLA-B27 positive juvenile onset active spondyloarthropathy. J Rheumatol. 2000 Jun;27(6):1538–1541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald T. T., Hutchings P., Choy M. Y., Murch S., Cooke A. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma production measured at the single cell level in normal and inflamed human intestine. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Aug;81(2):301–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb03334.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maksymowych W. P., Gorodezky C., Olivo A., Alaez C., Wong C., Burgos-Vargas R., Sanchez-Corona J., Ramos-Remus C., Russell A. S. HLA-DRB1*08 influences the development of disease in Mexican Mestizo with spondyloarthropathy. J Rheumatol. 1997 May;24(5):904–907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malleson P. N., Fung M. Y., Rosenberg A. M. The incidence of pediatric rheumatic diseases: results from the Canadian Pediatric Rheumatology Association Disease Registry. J Rheumatol. 1996 Nov;23(11):1981–1987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masi A. T. Do sex hormones play a role in ankylosing spondylitis? Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1992 Feb;18(1):153–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mielants H., Veys E. M., Cuvelier C., De Vos M., Goemaere S., De Clercq L., Schatteman L., Elewaut D. The evolution of spondyloarthropathies in relation to gut histology. II. Histological aspects. J Rheumatol. 1995 Dec;22(12):2273–2278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mielants H., Veys E. M., Cuvelier C., De Vos M., Goemaere S., De Clercq L., Schatteman L., Gyselbrecht L., Elewaut D. The evolution of spondyloarthropathies in relation to gut histology. III. Relation between gut and joint. J Rheumatol. 1995 Dec;22(12):2279–2284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mielants H., Veys E. M., Cuvelier C., De Vos M., Goemaere S., Maertens M., Joos R. Gut inflammation in children with late onset pauciarticular juvenile chronic arthritis and evolution to adult spondyloarthropathy--a prospective study. J Rheumatol. 1993 Sep;20(9):1567–1572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mielants H., Veys E. M., Joos R., Cuvelier C., De Vos M. Repeat ileocolonoscopy in reactive arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1987 Jun;14(3):456–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mielants H., Veys E. M., Joos R., Noens L., Cuvelier C., De Vos M. HLA antigens in seronegative spondylarthropathies. Reactive arthritis and arthritis in ankylosing spondylitis: relation to gut inflammation. J Rheumatol. 1987 Jun;14(3):466–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minden K., Kiessling U., Listing J., Niewerth M., Döring E., Meincke J., Schöntube M., Zink A. Prognosis of patients with juvenile chronic arthritis and juvenile spondyloarthropathy. J Rheumatol. 2000 Sep;27(9):2256–2263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murch S. H., Braegger C. P., Walker-Smith J. A., MacDonald T. T. Distribution and density of TNF immunoreactivity in chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1995;371B:1327–1330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray K. J., Grom A. A., Thompson S. D., Lieuwen D., Passo M. H., Glass D. N. Contrasting cytokine profiles in the synovium of different forms of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile spondyloarthropathy: prominence of interleukin 4 in restricted disease. J Rheumatol. 1998 Jul;25(7):1388–1398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray K. J., Luyrink L., Grom A. A., Passo M. H., Emery H., Witte D., Glass D. N. Immunohistological characteristics of T cell infiltrates in different forms of childhood onset chronic arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1996 Dec;23(12):2116–2124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäki-Ikola O., Lahesmaa R., Heesemann J., Merilahti-Palo R., Saario R., Toivanen A., Granfors K. Yersinia-specific antibodies in serum and synovial fluid in patients with Yersinia triggered reactive arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1994 Aug;53(8):535–539. doi: 10.1136/ard.53.8.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäki-Ikola O., Nissilä M., Lehtinen K., Granfors K. IgA class serum antibodies against three different Klebsiella serotypes in ankylosing spondylitis. Br J Rheumatol. 1998 Dec;37(12):1299–1302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäki-Ikola O., Nissilä M., Lehtinen K., Leirisalo-Repo M., Toivanen P., Granfors K. Antibodies to Klebsiella pneumoniae, Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis in the sera of patients with axial and peripheral form of ankylosing spondylitis. Br J Rheumatol. 1995 May;34(5):413–417. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/34.5.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäki-Ikola O., Yli-Kerttula U., Saario R., Toivanen P., Granfors K. Salmonella specific antibodies in serum and synovial fluid in patients with reactive arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1992 Jan;31(1):25–29. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/31.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oen K., Postl B., Chalmers I. M., Ling N., Schroeder M. L., Baragar F. D., Martin L., Reed M., Major P. Rheumatic diseases in an Inuit population. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Jan;29(1):65–74. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco-Tena C., Alvarado De La Barrera C., López-Vidal Y., Vázquez-Mellado J., Richaud-Patin Y., Amieva R. I., Llorente L., Martínez A., Zúiga J., Cifuentes-Alvarado M. Bacterial DNA in synovial fluid cells of patients with juvenile onset spondyloarthropathies. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2001 Aug;40(8):920–927. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/40.8.920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazmany L., Rowland-Jones S., Huet S., Hill A., Sutton J., Murray R., Brooks J., McMichael A. Genetic modulation of antigen presentation by HLA-B27 molecules. J Exp Med. 1992 Feb 1;175(2):361–369. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.2.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepmueller P. H., Moore T. L. Juvenile spondyloarthropathies. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2000 Jul;12(4):269–273. doi: 10.1097/00002281-200007000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Present D. H., Rutgeerts P., Targan S., Hanauer S. B., Mayer L., van Hogezand R. A., Podolsky D. K., Sands B. E., Braakman T., DeWoody K. L. Infliximab for the treatment of fistulas in patients with Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med. 1999 May 6;340(18):1398–1405. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199905063401804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prieur A. M. Spondyloarthropathies in childhood. Baillieres Clin Rheumatol. 1998 May;12(2):287–307. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3579(98)80020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. M. Analysis of a pediatric rheumatology clinic population. J Rheumatol. 1990 Jun;17(6):827–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. M., Petty R. E. A syndrome of seronegative enthesopathy and arthropathy in children. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Sep;25(9):1041–1047. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. M., Petty R. E., Oen K. G., Schroeder M. L. Rheumatic diseases in Western Canadian Indian children. J Rheumatol. 1982 Jul-Aug;9(4):589–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scofield R. H., Kurien B., Gross T., Warren W. L., Harley J. B. HLA-B27 binding of peptide from its own sequence and similar peptides from bacteria: implications for spondyloarthropathies. Lancet. 1995 Jun 17;345(8964):1542–1544. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)91089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scofield R. H., Warren W. L., Koelsch G., Harley J. B. A hypothesis for the HLA-B27 immune dysregulation in spondyloarthropathy: contributions from enteric organisms, B27 structure, peptides bound by B27, and convergent evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9330–9334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheerin K. A., Giannini E. H., Brewer E. J., Jr, Barron K. S. HLA-B27-associated arthropathy in childhood: long-term clinical and diagnostic outcome. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Sep;31(9):1165–1170. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieper J., Braun J. Pathogenesis of spondylarthropathies. Persistent bacterial antigen, autoimmunity, or both? Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Nov;38(11):1547–1554. doi: 10.1002/art.1780381105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieper J., Braun J., Wu P., Kingsley G. T cells are responsible for the enhanced synovial cellular immune response to triggering antigen in reactive arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Jan;91(1):96–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb03361.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieper J., Kingsley G., Palacios-Boix A., Pitzalis C., Treharne J., Hughes R., Keat A., Panayi G. S. Synovial T lymphocyte-specific immune response to Chlamydia trachomatis in Reiter's disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 May;34(5):588–598. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon A. K., Seipelt E., Wu P., Wenzel B., Braun J., Sieper J. Analysis of cytokine profiles in synovial T cell clones from chlamydial reactive arthritis patients: predominance of the Th1 subset. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Oct;94(1):122–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb05988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symmons D. P., Jones M., Osborne J., Sills J., Southwood T. R., Woo P. Pediatric rheumatology in the United Kingdom: data from the British Pediatric Rheumatology Group National Diagnostic Register. J Rheumatol. 1996 Nov;23(11):1975–1980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taccetti G., Trapani S., Ermini M., Falcini F. Reactive arthritis triggered by Yersinia enterocolitica: a review of 18 pediatric cases. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1994 Nov-Dec;12(6):681–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Bosch Filip, Kruithof Elli, Baeten Dominique, Herssens Annemie, de Keyser Filip, Mielants Herman, Veys Eric M. Randomized double-blind comparison of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor alpha (infliximab) versus placebo in active spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Mar;46(3):755–765. doi: 10.1002/art.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Bosch F., Kruithof E., Baeten D., De Keyser F., Mielants H., Veys E. M. Effects of a loading dose regimen of three infusions of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor alpha (infliximab) in spondyloarthropathy: an open pilot study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000 Jun;59(6):428–433. doi: 10.1136/ard.59.6.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]