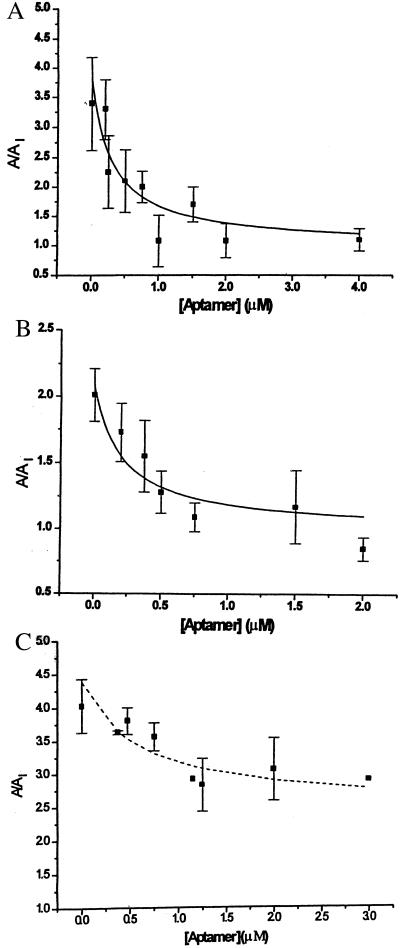
Figure 3.
Alleviation by aptamer II-3 of receptor inhibition by MK-801. The whole-cell current corrected for receptor desensitization was determined by the cell-flow technique (22). At a constant concentration of carbamoylcholine, the ratio of the maximum current amplitudes obtained in the absence, A, and presence, AI, of a constant concentration of MK-801 was determined as a function of the concentration of aptamer II-3 (22°C, −60 mV, and pH 7.4). The cell was preequilibrated with aptamer II-3 for 2 s. Each data point represents the average of two to three experiments by using on the average two cells per point. Eq. III-A was used to evaluate KI(obs) and KA(obs), the observed dissociation constants of the inhibitor and the aptamer, respectively. (A) Constant concentrations of 100 μM carbamoylcholine and 500 μM MK-801. The cells were preequilibrated with 500 μM MK-801 for 200 ms. KI(obs) = 180 ± 44 μM; KA(obs) = 0.32 ± 0.15 μM. (B) Constant concentrations of 500 μM carbamoylcholine and 300 μM MK-801. The cell was preequilibrated with 300 μM MK-801 for 200 ms. KI(obs) = 280 ± 50 μM; KA(obs) = 0.14 ± 0.07 μM. (C) Constant concentrations of 100 μM carbamoylcholine and 150 μM MK-801. The cell was preequilibrated with 150 μM MK-801 for 4 s. KI(obs) = 189 ± 74 μM; KII(obs) = 103 ± 23 μM; KA(obs) = 0.6 ± 0.1 μM, where KII(obs) is the inhibitor dissociation constant from the slowly equilibrating second inhibitory site. Experimental conditions were as described in Fig. 2 legend and in Materials and Methods (see also Eq. III-A, -B).