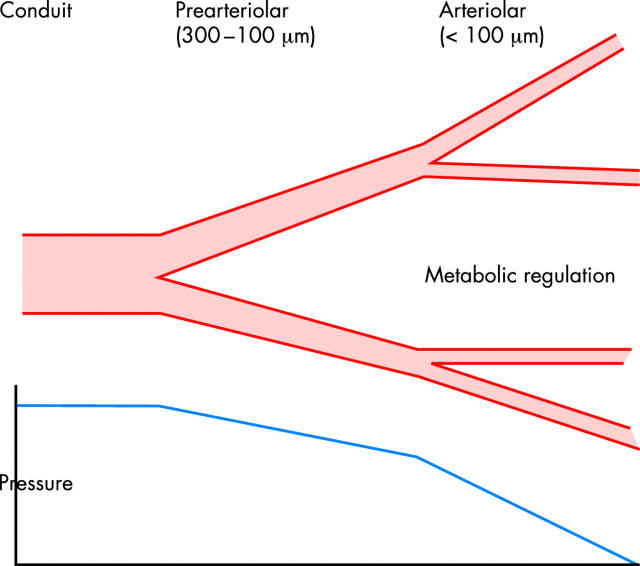
Figure 2.
Resistance to coronary flow is seen in two compartments. Normal epicardial coronary arteries are conduit vessels offering virtually no resistance to flow. The pre-arteriolar segments (~300–100 μm) offer variable resistance to flow and are regulated by a number of factors including nitric oxide. The arteriolar segment (< 100 μm) offers the greatest amount of resistance to flow and is the site of metabolic regulation facilitating the increase in flow with exercise.