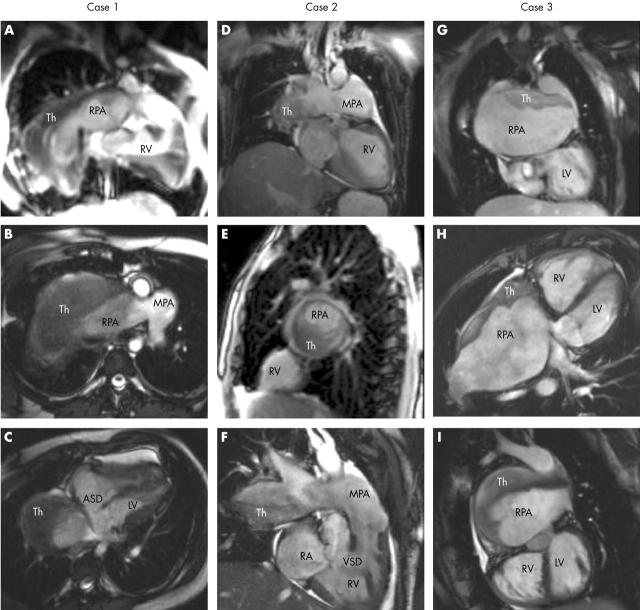
Figure 2.
True fast imaging steady precession magnetic resonance images of each patient. ASD, atrial septal defect; MPA, main pulmonary artery; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricle; Th, thrombus; VSD, ventricular septal defect. Case 1: (A) coronal slice showing the large RPA with Th;(B) transaxial slice showing the bifurcation of the MPA, with the RPA almost completely full of Th; (C) oblique transaxial cut in early systole showing the ASD. Case 2: (D) coronal slice; (E) sagittal slice through right lung, with Th occluding the majority of the RPA lumen; (F) oblique coronal slice showing the VSD. Case 3: (G) coronal slice with Th on the roof of the large RPA, with atrial baffles partly seen adjacent to the LV; (H) oblique transaxial slice showing anterior RV (systemic ventricle), posterior LV (pulmonary ventricle), and huge RPA with clot also anterior; (I) sagittal view from the left, showing the relation of LV to RPA.