Figure 1.
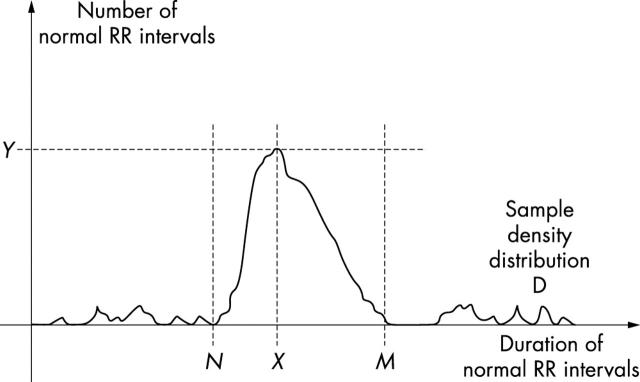
Measurement of geometric time domain indices of heart rate variability (HRV). To perform geometric measures on the NN interval histogram, the sample density distribution D is constructed, which assigns the number of equally long NN intervals to each value of their lengths. The most frequent NN interval length X is established—that is, Y = D(X) is the maximum of the sample density distribution D. The HRV triangular index is the value obtained by dividing the area integral of D by the maximum Y. When the distribution D with a discrete scale is constructed on the horizontal axis, the value is obtained according to the formula HRV index = (total number of all NN intervals)/Y. For the computation of the triangular interpolation of NN intervals (TINN) measure, the values N and M are established on the time axis and a multi-linear function q constructed such that q(t) = 0 for t N and t M and q(X) = Y, and such that the integral 0 + D(t) − q(t))2 dt is the minimum among all selections of all values N and M. The TINN measure is expressed in milliseconds and given by the formula TINN = M − N. Reproduced with permission from Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Circulation 1996;93:1043–65.