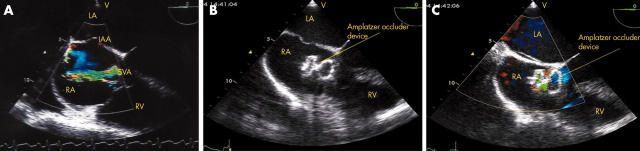
A 36 year old man was admitted with a four week history of worsening exertional dyspnoea and peripheral oedema. Transoesophageal echocardiography (TOE) revealed a ruptured aneurysm of the non-coronary sinus of Valsalva (SVA) protruding into the right atrium with a significant systemic to pulmonary shunt associated with enlargement of the right atrium and right ventricle. There was also an incidental finding of an interatrial septal aneurysm and patent foramen ovale (panel A). The patient underwent percutaneous closure of the ruptured sinus of Valsalva aneurysm using a 14 mm Amplatzer septal occluder device (panel B). This achieved a good result with a rapid improvement in the patient’s symptoms. There was only a mild residual shunt seen on TOE following the closure (panel C).
Transcatheter closure can be an effective treatment for a ruptured sinus of Valsalva aneurysm in selected cases.