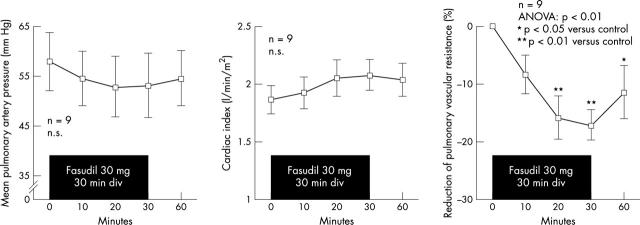
Figure 1.
Intravenous administration of fasudil slightly decreased pulmonary artery pressure (left panel) and increased cardiac index (middle panel), although there were no significant differences. However, fasudil significantly reduced pulmonary vascular resistance (right panel). Data are expressed as mean (SD) and analysed by ANOVA followed by a Fisher’s post hoc test.