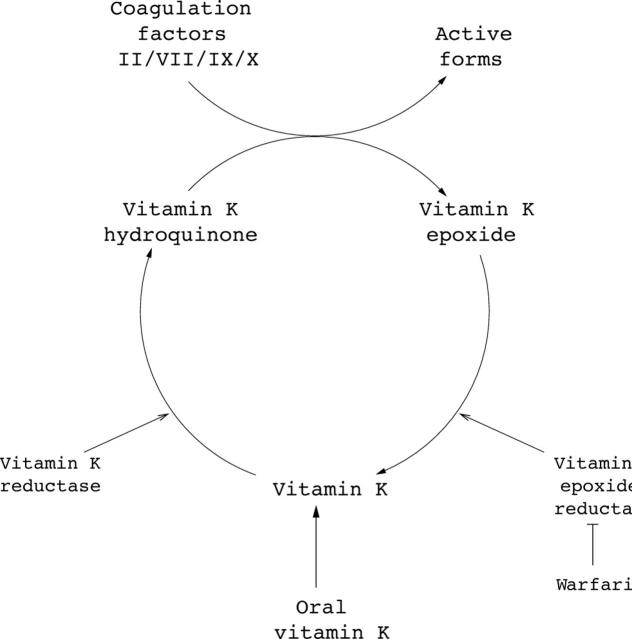
Figure 1.
Cyclical reduction and oxidation of vitamin K is inhibited by warfarin. Dietary vitamin K is reduced to vitamin K hydroquinone by vitamin K reductase. Vitamin K hydroquinone is then oxidised to vitamin K epoxide in a coupled reaction which results in the activation of coagulation factors II, VII, IX, and X. Vitamin K epoxide is then reduced back to vitamin K by vitamin K epoxide reductase (VKOR). This enzyme is inhibited by warfarin, leading to a block in the cycle, which results in a depletion in activated clotting factors.