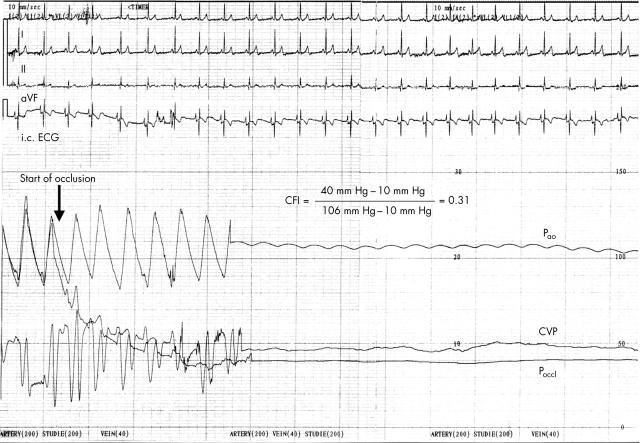
Figure 1.
Coronary collateral flow assessment with an intracoronary pressure guidewire in a patient with insulin dependent diabetes mellitus with angiographically normal coronary arteries. Collateral flow index (CFI), expressing collateral flow to the balloon occluded coronary artery relative to normal antegrade flow during vessel patency, is determined from mean aortic pressure (Pao), mean coronary pressure during balloon occlusion (Poccl), and central venous pressure (CVP) (phasic recordings of these pressures obtained during coronary patency are shown at left). After balloon occlusion, phasic and mean Poccl starts to decrease and plateaus at 40 mm Hg. Note the different scales for Pao, Poccl, and CVP. CFI is calculated as (Poccl – CVP)/(Pao – CVP). On the surface lead (I, II, aVF) and on the intracoronary ECG lead recorded through the sensor guidewire, no signs of myocardial ischaemia (ST segment changes) were observed during vessel occlusion when compared with the period before coronary occlusion. Additionally, the patient did not feel any chest pain during the one minute balloon occlusion.