Fig. 2.
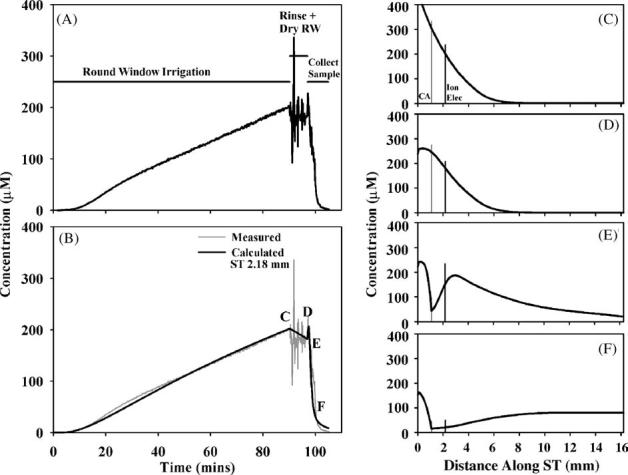
Interpretation of an experiment in which TMPA was loaded into perilymph by round window membrane (RWM) application of a 2 mM solution. (A) Concentration measured in the basal turn of scala tympani during RW irrigation of TMPA, rinsing and drying the RW niche, and during sample collection after perforation of the cochlear apex. (B) Simulation of the concentration measured at the cochlear location where the ion electrode was located. The measured curve is shown pale gray for comparison. (C-F) Calculated longitudinal distribution of TMPA along ST at the four time points indicated in panel (B). The locations of the cochlear aqueduct (CA) and of the TMPA-selective measurement electrode (Ion Elec) are indicated by vertical lines.
