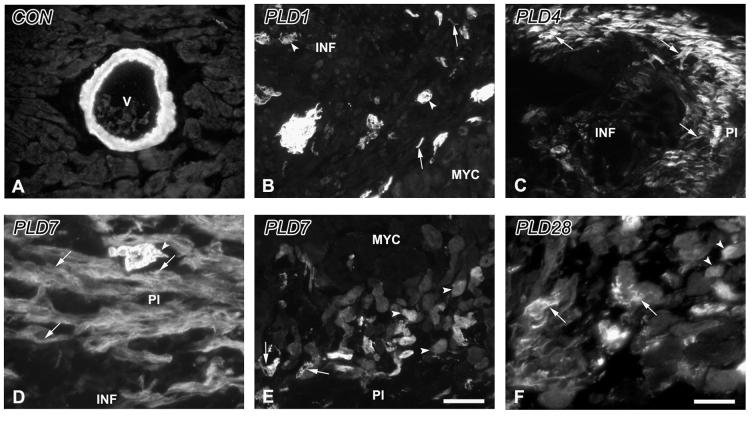
Figure 5.
α-Smooth muscle actin immunoreactivity in the control and infarcted ventricle. A. Control. α-smooth muscle actin immunoreactivity (α-SMA-ir) in non-infarcted myocardium is restricted to the smooth muscle walls of blood vessels (V). B. PLD1. α-SMA-ir is present within individual spindle-shaped cells (arrows) as well as in aggregates, and in blood vessels (arrowheads) within the infarct area (INF) adjacent to normal myocardium (MYC). C. PLD4. The edge of the peri-infarct (PI) is delineated by α-SMA-ir myofibroblasts (arrows). D. PLD 7. Expression of α-SMA-ir myofibroblasts (arrows) continues to be robust in the PI accompanied by neovascularizing blood vessels (arrowhead). E. PLD7. α-SMA-ir is observed in blood vessels (arrow) and cardiomyocytes (arrowheads) at the transition between the PI and the adjacent MYC. F. PLD 28. α-SMA-ir myofibroblasts (arrows) are reduced in number, while cardiomyocytes adjacent to scar tissue maintain their expression of this protein (arrowheads). Scale bar in E is 30 μm for panels A-C, E; scale bar in F is 15 μm for panels D, F.