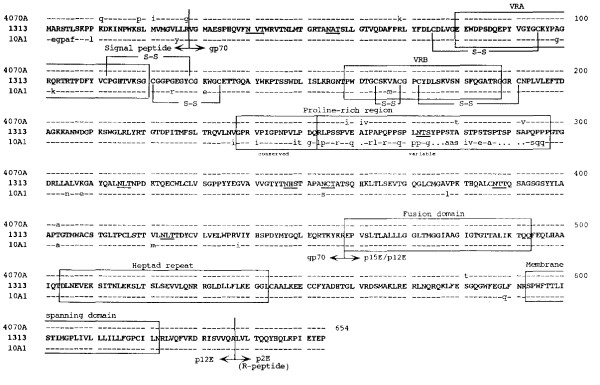
Figure 2.
Relationship of MuLV 1313 gPr80 Env protein with those of other amphotropic MuLV's. All deduced amino acid sequences of the MuLV 1313 gPr80 Env proteins and related amphotropic MuLV strains 4070A, and 10A-I were aligned using progressive, pair-wise alignments implemented in the Pileup and the Gap programs of the Wisconsin Package (version 9.0), Genetics Computer Group (GCG), Madison, WI [63-67, 80]. The amino acid sequences of MuLV 1313 Env protein are shown in its entirety (represented in bold, capital letters using the standard single-letter symbols). Amino acid positions that are in total agreement with MuLV 1313 Env are indicated with a dash (-) and differences are represented as small letters. Periods (·) in the 10A-I Env protein sequence indicate spaces that were introduced to maximize the alignment. Boundaries of the Env signal peptide (Leader) and the mature processed proteins are labeled and indicated with bold vertical lines. Major landmarks of the extracellular gp70 surface (SU) protein include the (i) variable region A (VRA), (ii) VRB and (iii) proline-rich region. Major landmarks of the p15E transmembrane™ protein include the (i) fusion, (ii) heptad repeat, (iii) membrane spanning and (iv) the R-peptide or p2E domains. Eight potential N-linked glycosylation sites (N, X, S/T) in the SU proteins of the MuLV 1313 and 4070A are underlined. Disulfide linkages shown at the N-terminus of SU are based on those deduced for the polytropic envelope protein [81]. The boundaries of the various elements included in this diagram are based on previously published work [51, 82, 83]. Accession numbers for each of the env genes used in this analysis are MuLV 1313 (AF411814), M33469 for the naturally occurring amphotropic virus 4070 and M33470 for the recombinant amphotropic virus 10A-1.