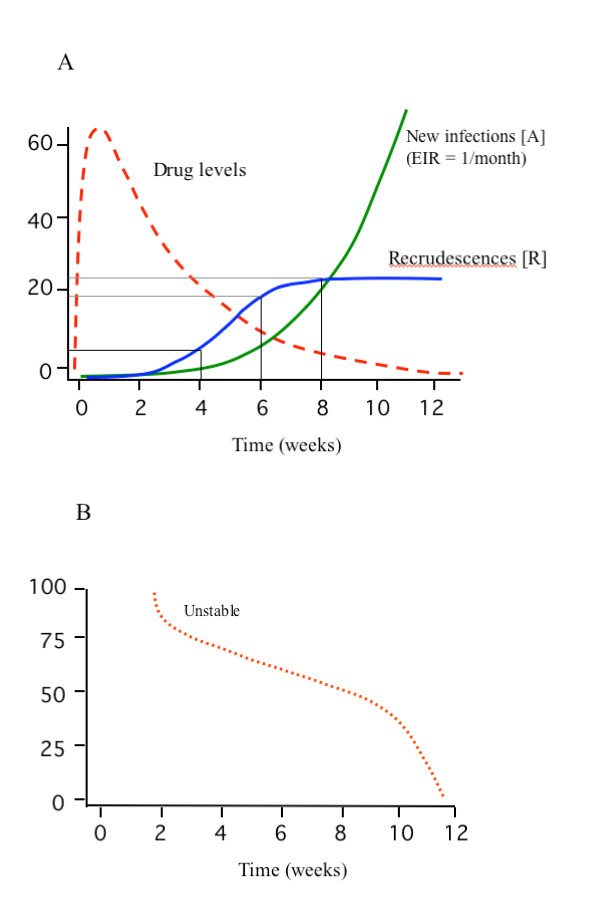
Figure 4.
a and b. Simulated example of a clinical trial evaluation of a slowly eliminated antimalarial drug (e.g. mefloquine) with a 23% failure rate evaluated in an area with high malaria transmission (EIR 12/year) (upper panel). The apparent failure rate based on genotyping at 4 weeks is 3% and at 6 weeks is 15%. All patients are eventually reinfected once the drug has been eliminated and the prophylactic effect exhausted. There is a non-linear relationship between recrudescences and reinfections. Figure 4b shows the proportion of recurrent infections that are recrudescences.