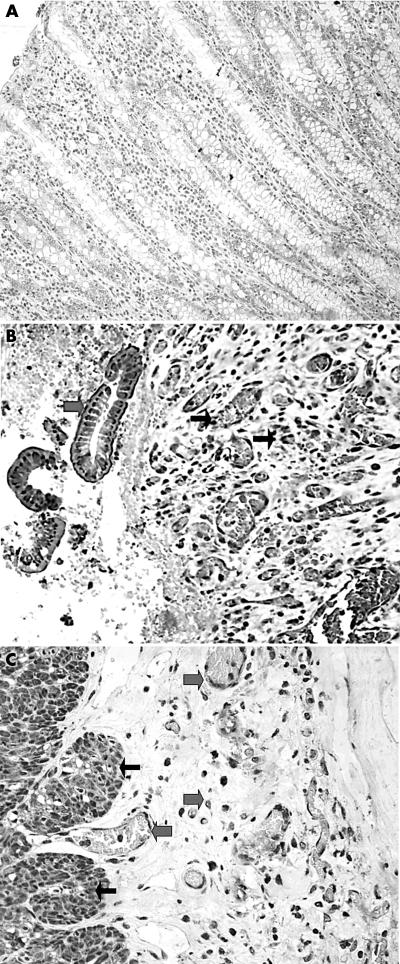
Figure 1.
(A) Normal intestinal mucosa showed no staining for hypoxia inducible factor 2α (HIF2α). (B) Intense and diffuse nuclear/cytoplasmic expression of HIF2α in degenerative epithelium (thick arrows) and the underlining mucosa (vessels and fibroblasts; thin arrows) in Crohn’s disease (CD). (C) Strong and diffuse nuclear/cytoplasmic expression of HIF2α in myocytes (thin arrows), endothelial cells, and serosal stromal cells (thick arrows) in CD. (D) Intense but focal expression of HIF1α (epithelium and fibroblasts; thick arrows) in ulcerative colitis on a background of negative reactivity (epithelium and stroma; thin arrows).