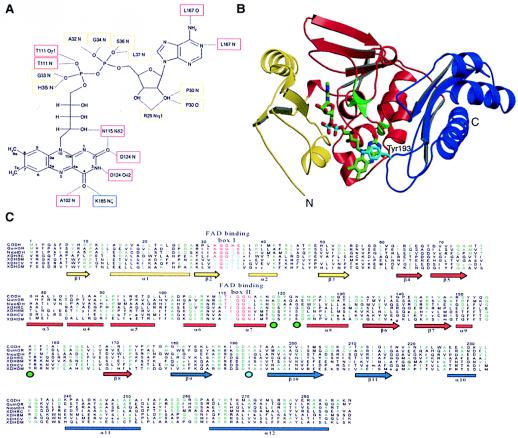
Figure 5.
Structure of the M subunit. (A) Molecular interactions of FAD in the M subunit. Atoms of the isoalloxazine ring are labeled. Residues binding the FAD cofactor through hydrogen bonds are marked, and boxes around the labels give the colors of the domains that harbor the corresponding residue. Whereas the N-terminal domain (yellow boxes) binds only to the dinucleotide portion of FAD, the middle domain (red boxes) interacts also with the riboflavin part. The C-terminal domain (blue box) shows only a single hydrogen bond to FAD. (B) Fold of the M subunit. The N-terminal domain is shown in yellow, the middle domain in red, and the C-terminal domain in blue. Tyr193M shields the isoalloxazine ring and is shown in cyan. The positions of residues corresponding to the rosy mutant strains of Drosophila melanogaster that resulted in an altered affinity to bind NAD+ in xanthine dehydrogenase are shown as green enlargements of the Cα chain and have a green circle under their position in C. (C) Sequence alignment of the M polypeptide of CO dehydrogenase with the corresponding representative parts from other members of the molybdenum hydroxylase family: CODH, CO dehydrogenase from Oligotropha carboxidovorans (coxM, Swall: Q51323); QuinOR, quinoline 2-oxidoreductase from Pseudomonas putida (qorM, Swall: P72222); NicotDH, nicotine dehydrogenase from Arthrobacter nicotinovorans (ndhA, Swall: Q59127); XDHRC, xanthine dehydrogenase from Rhodobacter capsulatus (xdhA, Swall: O54050); XDHBM, xanthine dehydrogenase from Bombyx mori (Swall: Q17209); XDHCV, xanthine dehydrogenase from Calliphora vicina (xdh, Swall: XDH CALVI); XDHDM, xanthine dehydrogenase from Drosophila melanogaster (xdh, Swall: XDH DROME). Two boxes highlighting residues responsible for FAD binding in the M subunit are shown in red and blue. They correspond to fingerprints for FAD-binding by enzymes of the molybdenum hydroxylase family and define a FAD-binding motif similar to the motifs found for the vanillyl alcohol oxidase family of flavoproteins. The secondary structure is represented by arrows for β-sheets and bars for α-helices, in domain colors (B). Residues appearing at least three times in a row are colored in green. The position of Tyr193M is marked by a cyan circle below the aligned sequences.