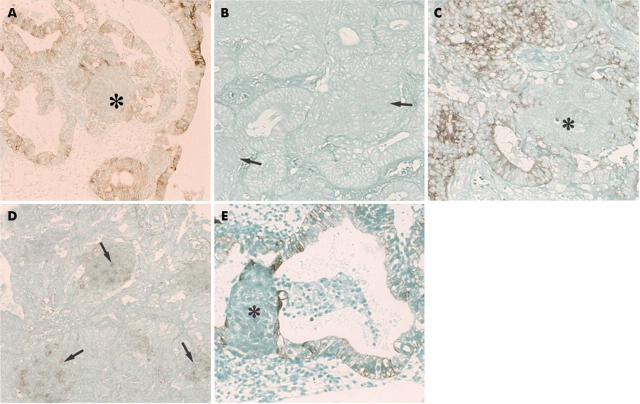
Figure 2.
(A) Immunohistochemistry for cytokeratins (AE1/AE3 antibodies) in morules. The asterisk indicates the morules. No immunoreactivity was seen in the morules, although the glandular epithelial cells (atypical endometrial hyperplasia) were positive. Original magnification, ×100. (B) Immunohistochemistry for cytokeratin (antibody to cytokeratin 10) in morules. The morules and the adenocarcinoma components (atypical endometrial hyperplasia) were immunonegative. The arrows indicate the morules. Original magnification, ×150. (C) Immunohistochemistry for epithelial membrane antigen (EMA) in morules. The morules were negative for EMA (asterisk), but the glandular epithelial cells (endometrioid carcinoma) were positive. Original magnification, ×150. (D) Immunohistochemical demonstration of neurone specific enolase (NSE) in morules. Staining for NSE was strong in the morules (arrowheads) (endometrioid carcinoma). Original magnification, ×150. (E) Immunohistochemical demonstration of cytokeratin in morules. Cytokeratin (AE1/AE3 antibodies) was found in a few cells (asterisk) in morules, but serial sections revealed that they were glandular epithelial cells. Glandular epithelial cells were positively stained (atypical endometrial hyperplasia case). Original magnification, ×150.