Fig. 2. CoCoA N-terminus interacts with p300.
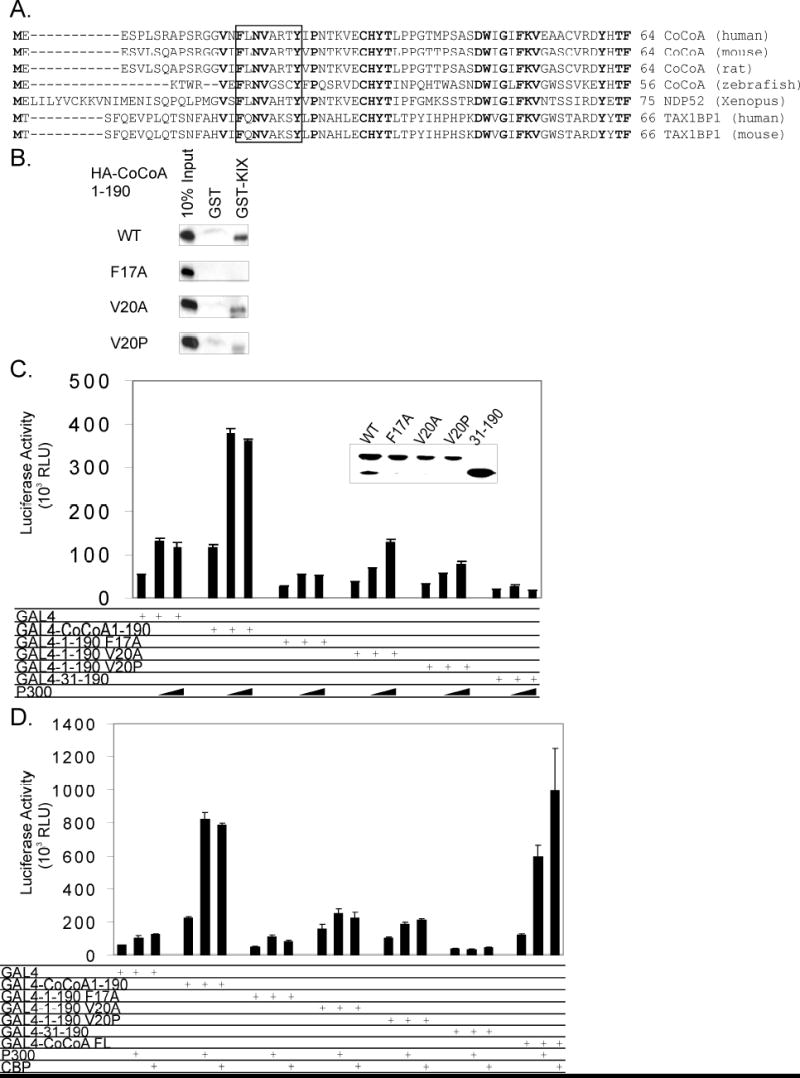
A, Sequence alignment of CoCoA and homologous proteins: human CoCoA (GenBank accession number NM_020898), mouse CoCoA (accession number NM_026192), rat CoCoA (accession number AAH81722), zebrafish CoCoA (accession number BC095162), Xenopus NDP52 (accession number AAG33628), human TAX1BP1 (accession number AAH50358), mouse TAX1BP1 (accession number AAH14798). Box shows the putative KIX-binding motif. Residues that are identical in all listed sequences are shown in bold. B, In vitro translated HA-tagged CoCoA (1-190) wild-type and mutants (F17A, V20A, V20P) were incubated with GST or GST-p300-KIX fusion proteins bound to glutathione-Sepharose beads in the presence of 300 mM NaCl. Bound proteins were eluted and analyzed by immunoblot with anti-HA antibody. C, 293T cells were transfected in 24-well plates with GK1-Luc reporter plasmids (150 ng), Gal4-DBD or Gal4-DBD-CoCoA fusion proteins (200 ng), and pCMV-p300 (50 or 100 ng) as indicated. Cell extracts were analyzed by immunoblot with antibodies against Gal4 (inset) or assayed for luciferase activity 48 h after transfection. D, 293T cells were transfected in 24-well plates with GK1- Luc reporter plasmids (150 ng), Gal4-DBD or Gal4-DBD-CoCoA fusion proteins (100 ng), and pCMV-p300 or CBP (50 ng) as indicated. Cell extracts were assayed for luciferase activity 48 h after transfection.
