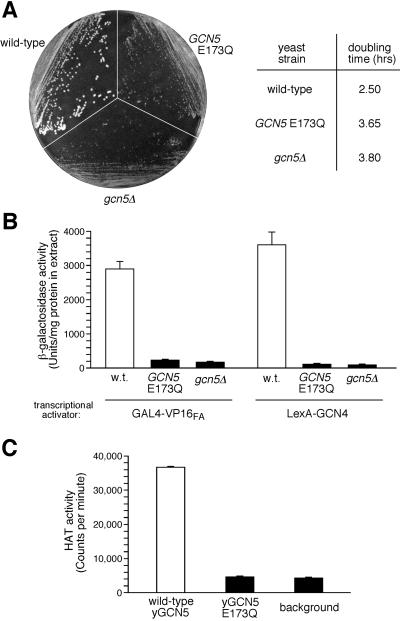
Figure 4.
Functional defects of the yGCN5 E173Q mutant and the putative role of Glu173 in catalysis. (A) Growth of yeast cells harboring empty vector (gcn5Δ), wild-type GCN5 plasmid, or GCN5 plasmid with a Glu-to-Gln mutation at residue 173 (E173Q). Strains were streaked on a minimal media plate (Left) or were grown in liquid minimal media at 30°C for determination of log-phase generation (doubling) times of the cells (Right). (B) Transcriptional activation in vivo. Shown are the activities of extracts from cells containing activator plasmid GAL4-VP16FA or LexA-GCN4 and the appropriate β-galactosidase reporter plasmid. (C) HAT activity assays in vitro. Purified yGCN5 and yGCN5-E173Q HAT domain proteins (0.1 μg) were used for liquid HAT assays with 3H-AcCoA and free histone substrates at pH 7.5 and 25°C.