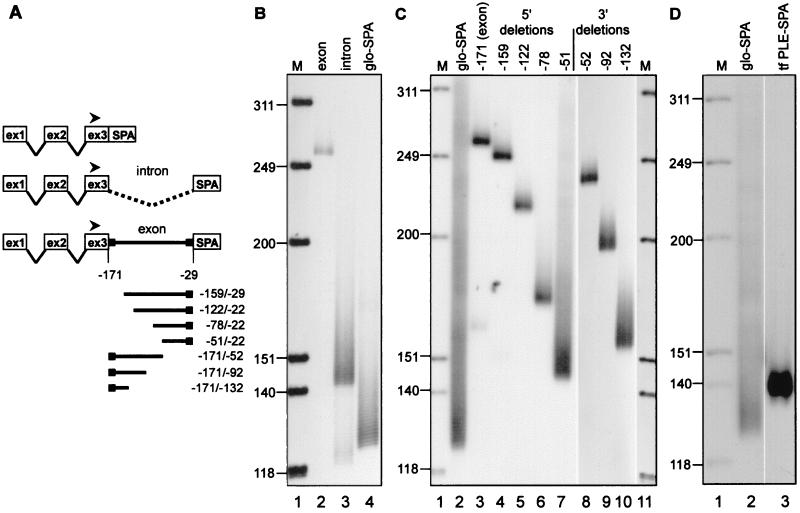
Figure 2.
Identification of the PLE in the transferrin gene. (A) The constructs that were transfected into LM(tk−) cells for analysis of poly(A) tail length on expressed mRNAs in B and C are diagrammed with the expression plasmid CMV-glo-SPA shown on top. The location of the radiolabeled globin exon 3 primer used for RT-PCR of all samples is indicated with a filled arrowhead. The numerical positions indicated on the diagram refer to the nucleotide locations within transferrin mRNA relative to the site of poly(A) addition. (B) Poly(A) tail lengths were determined for mRNAs expressed from constructs bearing the terminal transferrin exon (lane 2, exon), the terminal intron plus 13 bp of flanking exon sequence to retain functional splice sites (lane 3, intron), and vector control with no inserted transferrin DNA (lane 4, glo-SPA). M, molecular size marker HinfI-digested OX174 DNA. (C) Poly(A) tail lengths were determined for mRNAs expressed from constructs bearing nested 5′ and 3′ deletions of the terminal transferrin exon. The numbering at the top refers to the positions of the 5′ or 3′ ends relative to the site of poly(A) addition on transferrin mRNA. The poly(A) tail length of mRNA expressed from the vector control is shown in lane 2 (glo-SPA). M, molecular size marker HinfI-digested OX174 DNA. (D) Poly(A) tail lengths were determined for mRNA expressed from vector control (lane 2, glo-SPA) or vector carrying a fragment spanning nucleotides −82/−60 of transferrin mRNA inserted upstream of SPA (lane 3, tf PLE-SPA). M, molecular size marker HinfI-digested OX174 DNA.