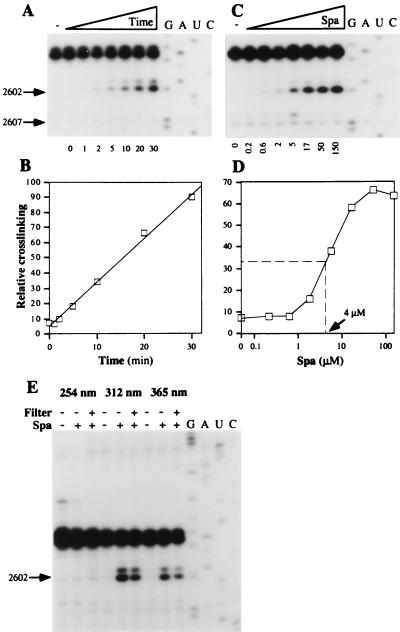
Figure 3.
Chemical characteristics of the sparsomycin crosslink. (A) Time dependence. 70S ribosomes.poly(U).N-Ac-Phe-tRNA (150 nM) and sparsomycin (50 μM) were complexed (see Materials and Methods) and irradiated at 365 nm for 1–30 min as indicated below the autoradiogram. G, A, U, and C denote sequencing tracks. (B) The reverse transcriptase stop at A2602 was quantified relative to the control band at G2607 in an Instant Imager (Packard) and was plotted as a function of the irradiation time. (C) Concentration dependence. Ribosomal complexes (30 nM) were irradiated at 365 nm for 20 min in the presence of increasing concentrations of sparsomycin (200 nM - 150 μM), indicated below the gel. (D) The reverse transcriptase stop at A2602 (in C) was quantified relative to the control band at G2607 in an Instant Imager and was plotted as a function of the sparsomycin concentration. (E) Wavelength-dependence. Ribosomal complexes (150 nM) and sparsomycin (50 μM) were mixed and irradiated at 254, 312, or 365 nm for 15 min (see Materials and Methods). When indicated (+ or −), a petri dish was used as a filter (<300 nm).