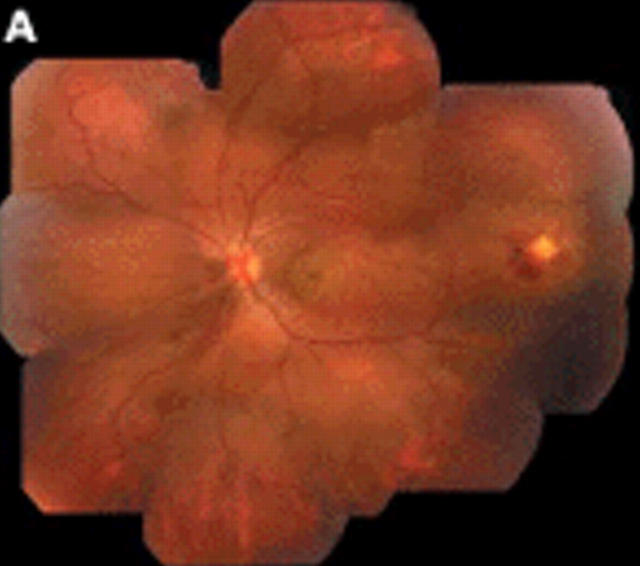
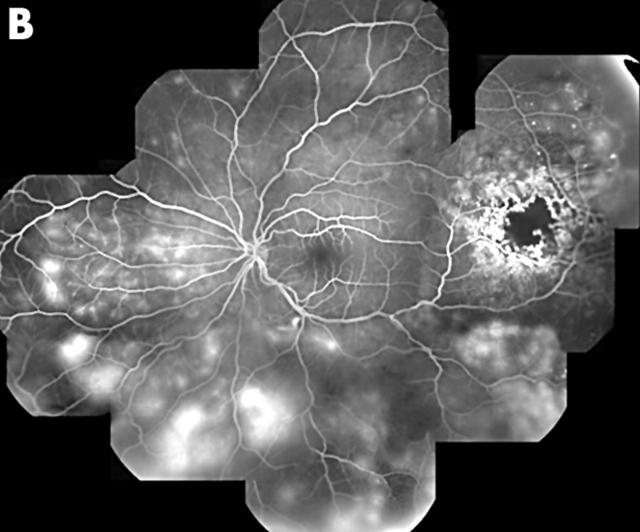
Figure 1.
(A) Composite clinical picture of the left eye demonstrated the presence of serous, neurosensory macular detachment, and mild lipid exudation. A well localised area of microvascular retinal changes was present in the temporal periphery. There was also a dependent, exudative, neurosensory detachment and mild lipid exudation throughout the fundus. (B) Composite fluorescein angiography photograph of the same eye confirmed the presence of vascular changes consistent with Coats’ disease. There was capillary non-perfusion, microaneurysm and telangiectasia formation, beading and irregularity of the larger vessel walls. Intraretinal vascular leakage was present throughout the fundus.