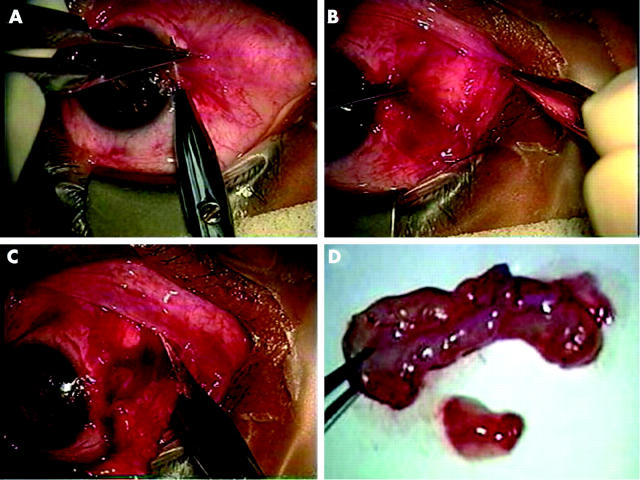
Figure 1.
Surgical procedures of removing subconjunctival fibrovascular tissue. In this representative case, the head is avulsed from the corneal surface from the limbus by a blunt dissection (A). The subconjunctival fibrovascular tissue grabbed by a fine forceps is dissected with a sharp scissors from the overlying epithelial tissue, which is also grabbed with another fine forceps (B). The subconjunctival tissue is then transected from the fornix, which was infiltrated with fat tissue in the nasal caruncle (C). The transected subconjunctival fibrovascular tissue is of several folds in size compared to that of the head and body (D).