Figure 1.
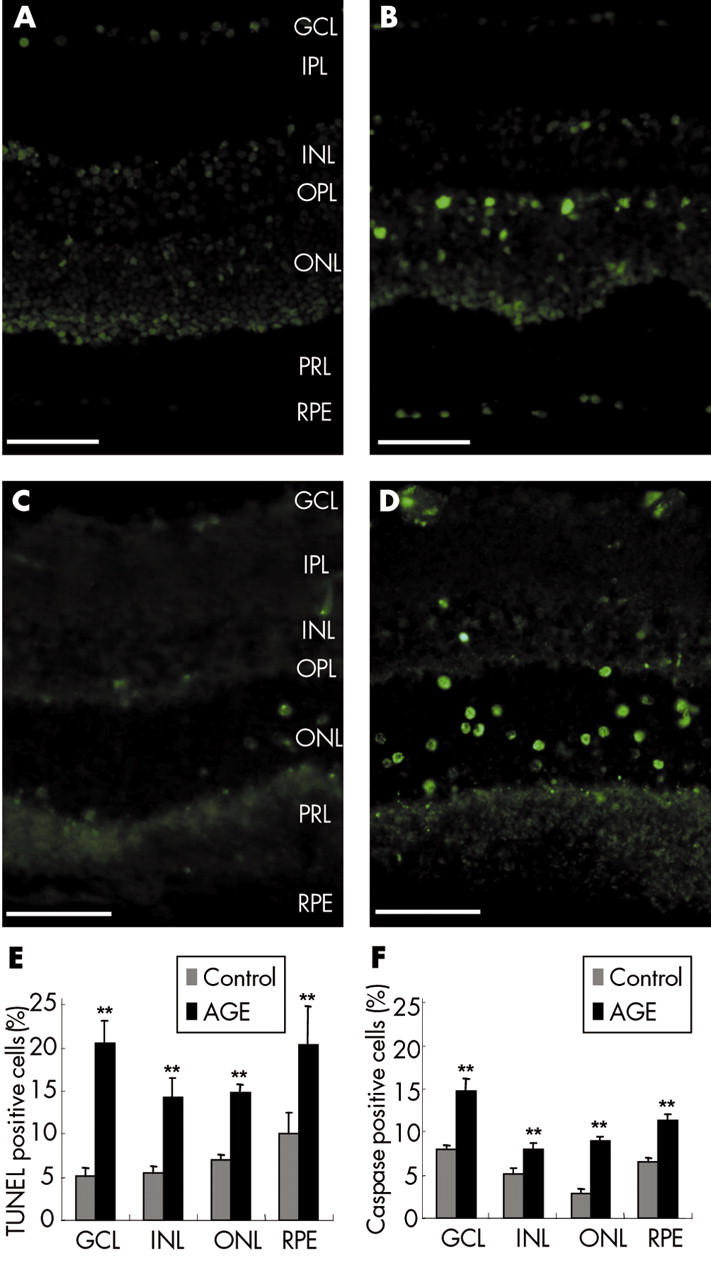
Retinal cell apoptosis induced by glycated BSA. Terminal dUTP nick end labelling (TUNEL-FITC) of cryostat sections from control retinal explants (A) or explants treated with glycated BSA (B). Immunolabelling for the active cleaved caspase-3 on cryostat sections from control retinal explants (C) and explants treated with glycated BSA (D). Note that small groups of adjacent TUNEL positive cells can be observed in the inner part of the outer nuclear layer in the retinal explant treated with glycated BSA (B) while these features are not found in the control retinal explant (A). (E) Quantification of the TUNEL positive retinal cells in control retinal explants (n = 7) and explants treated with glycated BSA (n = 7). (F) Quantification of cleaved active caspase-3 positive cells in control retinal explants (n = 7) and explants treated with glycated BSA (n = 7). In all retinal layers, the number of TUNEL and caspase-3 positive cells were significantly greater in retinal explants treated with glycated BSA than in control explants (p<0.001). GCL, ganglion cell layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; PRL, photoreceptor layer, RPE, retinal pigment epithelium. Errors bars indicate SEM. Scale bars represent 50 μm.
