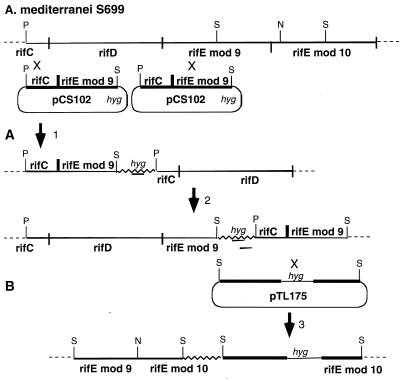
Figure 3.
Construction of rifD and rifE mutants. (A) The rifD mutant resulted from crossover 1 to produce a hygromycin-resistant strain in which the entire rifD gene has been deleted, which, in effect, produces a strain without the RifD and RifE subunits of the PKS, because transcription does not reinitiate downstream of rifC. The rifE module 9 mutant resulted from crossover 2 to produce a hygromycin-resistant strain in which module 9 for the rifE gene has been disrupted, which results in a strain without the RifE subunit of the PKS because transcription does not reinitiate downstream of rifD. (B) The rifE module 10 mutant resulted from crossover 3 to produce a hygromycin-resistant strain in which module 10 of the rifE gene has been disrupted, producing a strain with a truncated RifE protein. Thicker black lines represent the genomic DNA and the boundaries of the rif PKS genes. The thick, black line in pCS102 between rifC and rifE module 9 shows the place at which these two genes were fused. The jagged line presents the vector DNA. P, PstI; S, SstI; N, NcoI; Hyg, hygromycin resistance gene.