Figure 1. Illustration of an Isothermal Titration Calorimeter.
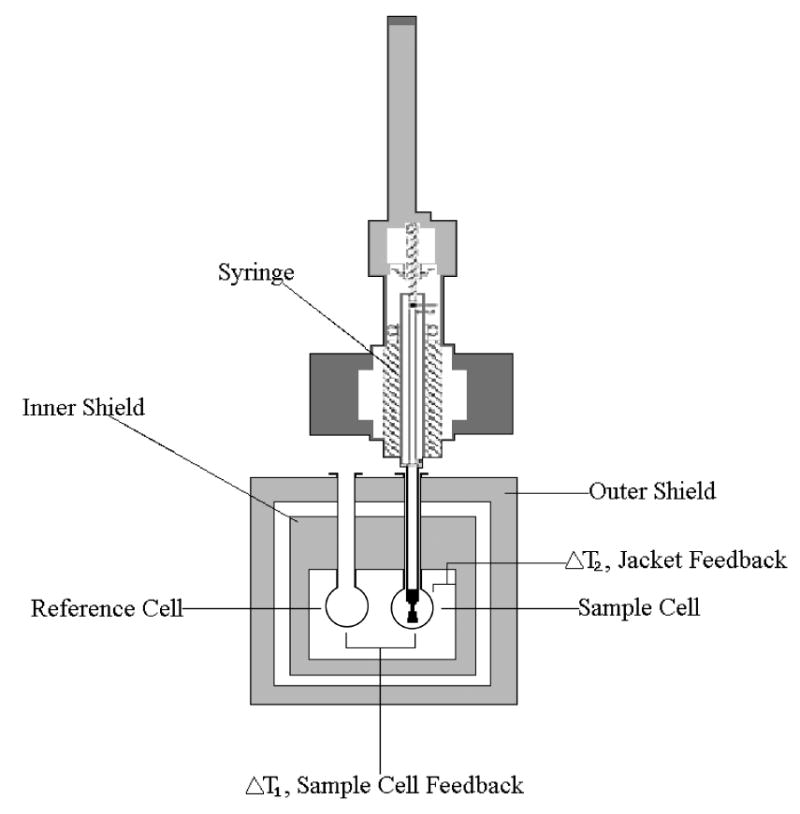
Two cells in an adiabatic environment are connected to the outside through narrow access tubes. A thermoelectric device measures the temperature difference between the two cells. A second device measures the difference in temperature between the cells and the jacket. During the process of a chemical reaction occurring in the sample cell, heat is generated or absorbed. The temperature difference between the sample and reference cells (ΔT1) is kept at zero by the addition of heat to the sample or reference cell. The integral of the power required to maintain ΔT1 = 0 over time is a measure of total heat resulting from the process being studied. A spinning syringe is used for injecting and subsequent mixing of the reactants in the experiment (VP-ITC MicroCalorimeter User’s Manual).
