Figure 1.
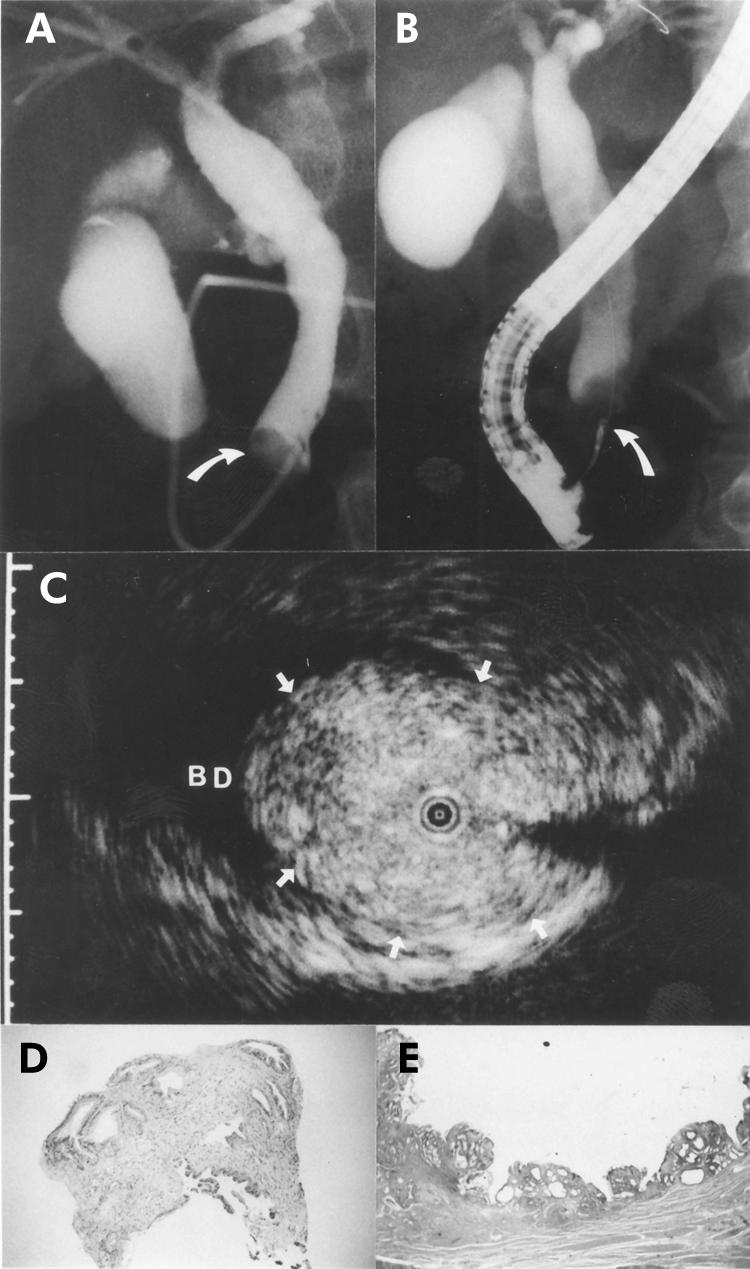
A 60 year old man with a polypoid lesion of the bile duct. The patient initially presented with obstructive jaundice and underwent endoscopic retrograde cholangiography. (A) Cholangiography showed a filling defect in the distal portion of the bile duct (arrow). (B) Endoscopic transpapillary bile duct biopsy was performed (arrow). (C) A frame from intraductal ultrasonography showed the probe in the bile duct (BD) within the ultrasonographic field of view. Note the narrow based polypoid lesion (arrows) with the normal structure of the bile duct. The narrow dot at the margin of the frame was 1.0 mm in width. (D) The histological findings of the biopsy specimen showed only inflammation (haematoxylin and eosin, ×10). (E) The histological findings of the resected specimen showed inflammatory polyp (haematoxylin and eosin, ×2).
