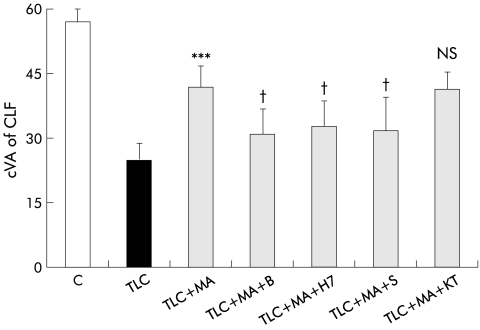
Figure 4.
Effect of inhibitors of protein kinase C (PKC), protein kinase A (PKA), and Ca2+ dependent signalling pathways on hepatoprotection induced by β-muricholate (MA) against taurolithocholate (TLC) induced decrease in canalicular vacuolar accumulation (cVA) of cholyl-lysyl-fluorescein (CLF). Couplets were incubated for 15 minutes at 37°C with dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO, control), 1,2-bis-(o-aminophenoxy)-ethene-N,N,N`,N`-tetra-acetate tetra-(acetomethyl)ester (BAPTA/AM (B)), H7, staurosporine (S), or KT5720 (KT). Then, TLC was added to dishes containing DMSO, and TLC+MA were added to the remaining dishes, and cells were incubated for another 30 minutes. cVA of CLF was then analysed. All values are means (SD) (n=5–6). The protective effect of MA on TLC induced cholestasis was significantly decreased by the presence of B, H7, and S, but not by KT. Significantly different from TLC, ***p<0.001; significantly different from TLC+MA, †p<0.05; NS, not significant.