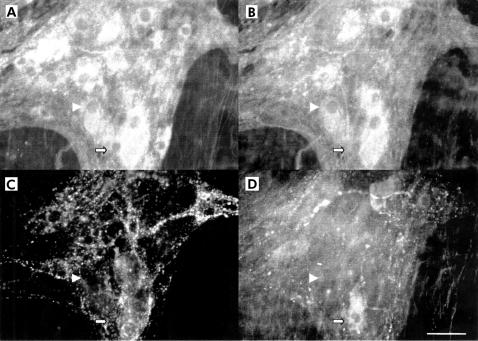
Figure 1.
Immunohistochemical detection of transmitter coding of human myenteric plexus from control patients. Quadruple labelling with antibodies against neurone specific enolase (NSE), choline acetyltransferase (ChAT), substance P (SP), and vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) performed in a myenteric ganglion showed various subpopulations. A ganglion was labelled with NSE to identify myenteric neurones (A). ChAT neurones (B) formed the largest population identified and were not usually co-localised with SP or VIP (arrowhead). No SP positive neurones (C) and few VIP positive neurones (D) were identified in this ganglion. VIP positive neurones were not co-localised with ChAT or SP (filled arrow). Scale bar: 25 μm.