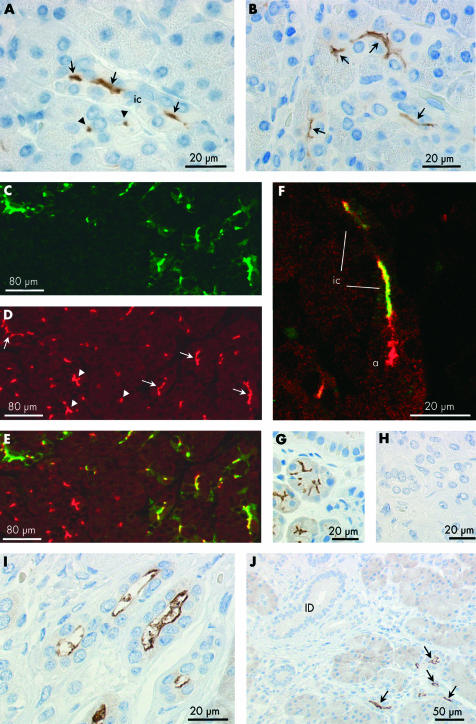
Figure 5.
Immunolocalisation of aquaporin 5 (AQP5) in intercalated and intralobular ducts of human pancreas. (A, B) Immunoperoxidase labelling of AQP5 at the apical membrane of intercalated ducts (ic) in longitudinal (arrows) and transverse (arrowheads) section. Both antirat and antihuman AQP5 antibodies gave the same labelling pattern. The field in (A) corresponds to fig 2G ▶ which shows AQP1 labelling in a contiguous section. (C) Immuno- fluorescence labelling of AQP5 (green) at the apical membrane of intercalated ducts. (D) Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) (red) at similar locations (arrows) and also in the lumen of the acini (arrowheads). (E) Merged images showing colocalisation of AQP5 and CFTR at the apical membrane of intercalated ducts (yellow). (F) Colocalisation of AQP5 (green) and CFTR (red) in the lumen of the intercalated duct (ic) leading from a single acinus. CFTR, but not AQP5, is seen at the apical membrane of the acinar cells (a). (G) Immunoperoxidase labelling of the apical membrane and secretory canaliculi of human submandibular acinar cells confirming the specificity of the AQP5 antibody. (H) Section of human pancreas exposed to the AQP5 antibody pre-adsorbed with the immunising peptide. (I) Immuno- peroxidase labelling of AQP5 at the apical membrane of intralobular duct cells in longitudinal profile. (J) Absence of AQP5 labelling in interlobular ducts (ID) despite strong labelling of intercalated and intralobular ducts (arrows).