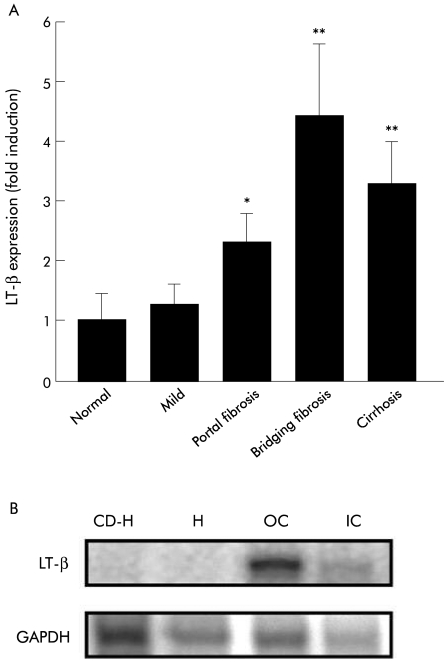
Figure 1.
(A) Expression of lymphotoxin β (LT-β) mRNA in liver in chronic hepatitis C. LT-β mRNA levels detected in liver biopsies from chronic hepatitis C patients increased significantly with fibrosis and cirrhosis. No significant difference was observed between control liver (n=5) and subjects with non-fibrotic liver damage (n=5). LT-β mRNA levels were 2.3-fold and 4.4-fold higher than control liver in subjects with portal fibrosis (n=5) and bridging fibrosis (n=5), respectively. LT-β mRNA levels were increased 3.3-fold in cirrhotic liver (n=5) compared with control liver. Results are expressed as mean (SEM) (*p=0.04, **p=0.02). (B) Ribonuclease protection analysis performed on RNA extracted from hepatocytes, oval cells, and inflammatory cells isolated from mice that received a choline deficient ethionine supplemented (CDE) diet for four weeks. LT-β mRNA is expressed by oval cells (O) and inflammatory cells (IC). LT-β mRNA was undetectable in normal hepatocytes (H) and CDE-treated hepatocytes (CD-H). GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.