Figure 1.
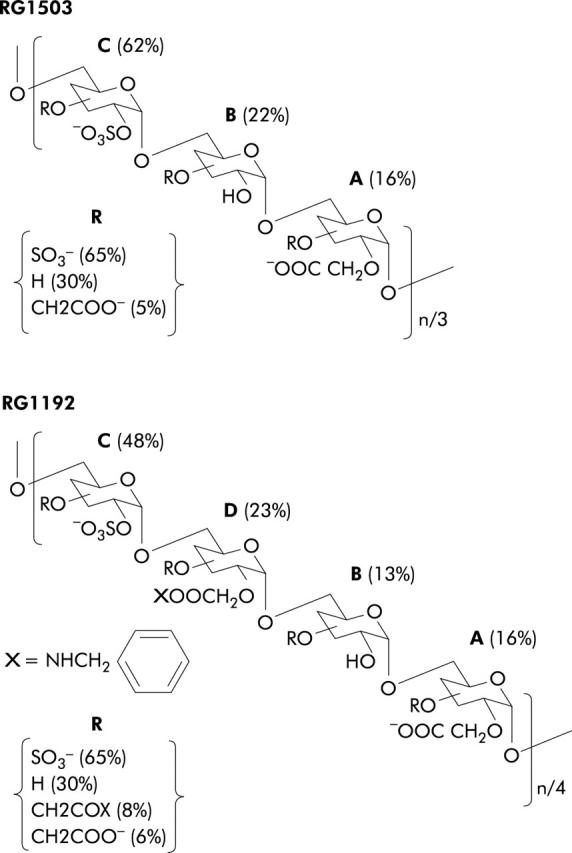
Schematic structure of dextran derivatives. Polymers were elaborated from T40 dextran by chemical substitutions, as described in materials and methods. Dextrans were substituted by carboxymethylation followed by O-sulphonation (RG1503) or by carboxymethylation followed by amidation with benzylamine and O-sulphonation (RG1192). The different percentages indicated were calculated from the degree of substitution (ds) relative to the position of each group in a glucosidic unit, as reported in table 2 ▶. For an easy representation, the substituted glucosidic units A, B, C, and D were arranged in an arbitrary combination. Their respective proportions (%) within each polymer were calculated according to the nature of the group at the C2 position. R is the proportion (%) of each substituted group at the C3 plus C4 positions.
