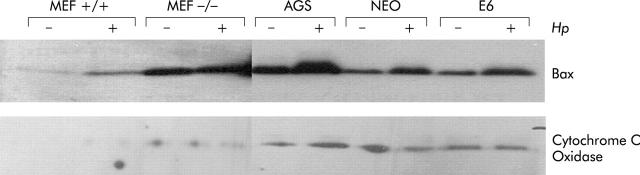
Figure 2.
Helicobacter pylori induced mitochondrial Bax translocation is dependent on ARF and partially on p53. Mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEF) from either ARF+/+ or ARF−/− mice, AGS, AGS-E6 (E6), and AGS-neo (NEO) cells were cocultured with H pylori for three hours (+) or cultured in medium alone as a control (−). Cytosolic and mitochondrial extracts were loaded onto sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gels followed by immunoblotting for Bax and cytochrome c oxidase. Bax translocated was integrated into mitochondrial membranes in ARF+/+ MEFs, AGS, and AGS-neo (3-, 2.4-, and 2.2-fold, respectively) but not into ARF−/− MEFs, and to a minimum in AGS-E6 cells (1.3-fold), suggesting that ARF, and to some extent p53, contribute to activation of Bax. Cytochrome c oxidase used as an internal control confirms the loading and quality of the lysates.