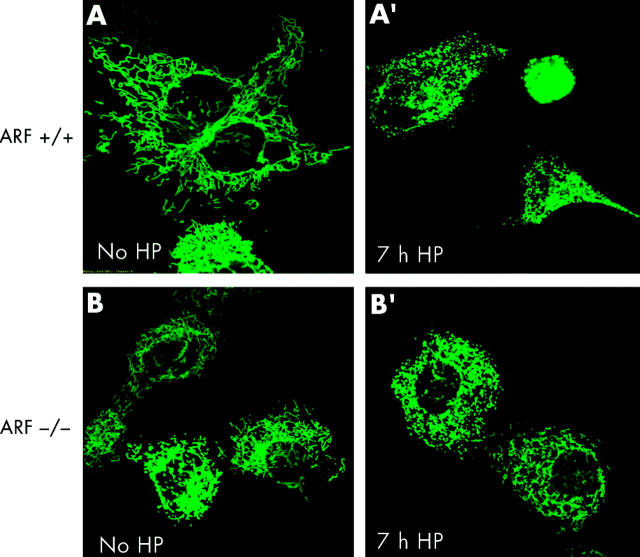
Figure 5.
Helicobacter pylori induced mitochondrial fragmentation. ARF+/+ mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) and ARF−/− MEFs transfected with mito-green fluorescent protein (GFP) were treated with H pylori and visualised by confocal microscopy. Mitochondrial morphology of ARF+/+ MEFs cells was assessed at seven hours after H pylori treatment by confocal microscopy. The gradual decrease in the percentage of cells featuring normal mitochondrial morphology was paralleled by an increasing percentage of cells exhibiting the punctiform phenotype. (A′) ARF+/+ MEFs undergoing profound changes in their mitochondrial phenotype during H pylori induced apoptosis are shown. In ARF+/+ MEF cells, the characteristic reticulotubular mitochondrial morphology (A) disintegrates into numerous round fragments of varying size (A′). In some cells, as exemplified by the bottom panel, the resulting punctiform mitochondria appear swollen, relative to the normally thin diameter of the mitochondrial tubules. (B) Mitochondrial morphology was also documented in mito-GFP transfected ARF−/− MEFs cells before (B) and after seven hours of H pylori treatment (B′). Mitochondria appear healthy and no obvious morphological changes were observed.