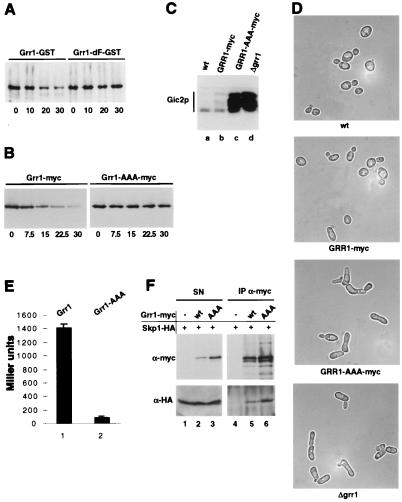
Figure 5.
An intact F-box is required for degradation and function of Grr1p. (A) The stability of a GST-tagged Grr1p mutant (Grr1p-dF-GST) deleted for the F-box (right four lanes) was compared with wild-type Grr1p-GST (left four lanes) by using CX. Expression of Grr1p-GST was followed by immunoblotting with antibodies specific for GST. (B) The stability of a Grr1p mutant (Grr1p-AAA-myc) harboring mutations in three conserved residues in the F-box (JMG61; Right) was compared with wild-type Grr1p-myc (JMG101; Left). Note that Grr1p-AAA-myc is stable. (C) Cells expressing Grr1p-AAA-myc were unable to degrade Gic2p. Accumulation and phosphorylation of the SCFGrr1 target Gic2p was analyzed in the following strains: lane a, wild-type (W303); lane b, GRR1-myc (JMG101); lane c, GRR1-AAA-myc (JMG61); and lane d, Δgrr1 (YM2957). (D) Morphology of cells expressing Grr1p-AAA-myc (JMG61; second panel from the top), Grr1p-myc (JMG101; third panel), or wild-type Grr1p (W303; top panel) and cells deleted for GRR1 (YM2957; bottom panel). Note that cells expressing Grr1p-AAA-myc exhibit an aberrant morphology characteristic for cells lacking SCFGrr1 function (29). (×2,000.) (E) The interaction between Skp1p and wild-type Grr1p (column 1) or Grr1p-AAA (column 2) was analyzed by two-hybrid assay. Bars show Miller units with standard deviations determined. (F) Extracts prepared from cells expressing Skp1p-HA and either wild-type Grr1p-myc (JMG101; lanes 2 and 5), Grr1p-AAA-myc (JMG61; lanes 3 and 6), or untagged Grr1p (W303; lanes 1 and 4) were immunoprecipitated (IP α-myc; right panels) with 9E10 antibodies and analyzed for the presence of Grr1p-myc (upper panels) or Skp1p-HA (lower panels) by immunoblotting. An aliquot of the supernatant (SN; left panels) before to immunoprecipitation was included as a control. Note that Grr1p-AAA-myc is able to co-immunoprecipitate with Skp1p-HA.