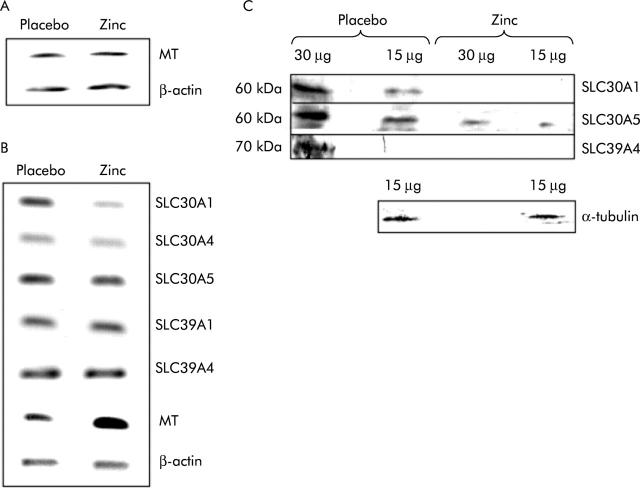
Figure 1.
Comparison of the expression of zinc related genes in peripheral blood monocytes and biopsies of human small intestine taken either after zinc supplementation or administration of placebo. (A) Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) products generated using primers specific to the transcripts indicated from poly-A+ RNA prepared from total monocyte RNA pooled from 17 volunteers. (B) RT-PCR products generated using primers specific to the transcripts indicated from poly-A+ RNA prepared from total RNA pooled from single intestinal biopsies from 17 volunteers. For (A) and (B), products generated from poly-A+ RNA prepared from biopsies following administration of placebo or zinc supplement are shown as indicated. PCR was carried out over a non-saturating number of cycles and thus band intensity is representative of the quantity of the specific transcript in the RNA sample. Three independent analyses of the relative expression level of each transcript in the two samples gave comparable results. MT, metallothionein. (C) Analysis by immunoblotting using antipeptide antibodies of expression in pooled biopsies from each of 17 volunteers of the zinc transporters SLC30A1, SLC30A5, and SLC39A4, and of α-tubulin, as indicated. For each sample either 15 μg or 30 μg of protein, as determined by Bradford analysis, were resolved by sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis prior to blotting. The result of analysis of samples prepared from biopsies following administration of placebo or the zinc supplement are shown as indicated.