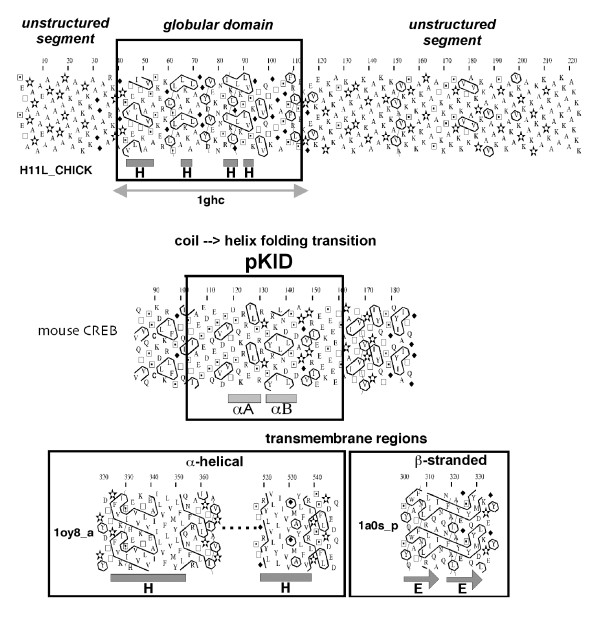
Figure 8.
Prediction of the limits of different protein domains through the HCA plot texture. Top panelA globular domain, preceded and followed by unstructured segments (histone H1, SW:H11L_CHICK, globular domain pdb 1ghc). The globular domain includes ~33 % of hydrophobic residues (V, I, L, F, M, Y, W), gathered into clusters whose lengths are typical of those of regular secondary structures. In contrast, no or only small hydrophobic clusters are present in the unstructured segments. The observed secondary structures are shown below the plot (H helix). Middle panelExample of an intrinsically disordered segment (phosphorylated kinase-inducible domain (pKID) of mouse CREB), which undergoes a coil --> helix transition upon binding to its partner (KIX domain of the coactivator CBP) [28]. Hydrophobic clusters suggest the presence of regular secondary (α-helices). Bottom panelSegments of membrane proteins, showing the typical texture associated with transmembrane α-helices (E.coli acriflavine resistance protein b; pdb 1oy8 (chain a), and transmembrane β-strands (S.typhimurium sucrose-specific protein; pdb 1a0s (chain p). A typical example of a HCA-based analysis of membrane proteins can be found in [44] (comparison of E.coli AmtB and human Rh proteins).