Figure 1.
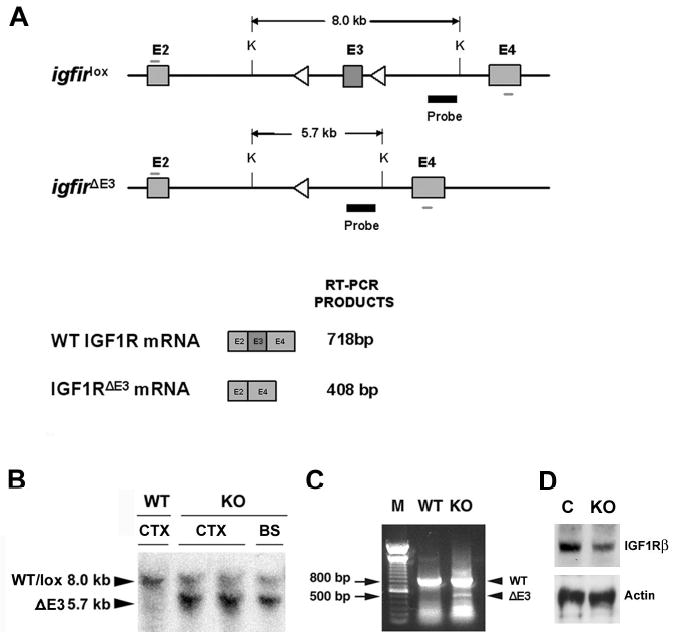
Schematic diagram of mutant igf1r genes, and representative genotype analyses of conditional igf1r mutant (KO) and wildtype (WT) mice. Panel A. Schematic diagram of mutant igf1r genes with loxed or deleted E3 (upper diagrams) and their mRNAs (lower diagrams). The exons of loxed (igf1rlox) or E3-deleted (igf1r E3) igf1r genes are represented by shaded boxes and their number labeled above each exon. Lox sequences were represented by open triangles. The position of a DNA probe used for Southern blot analysis is indicated by a thick black line, and the primers for RT-PCR are indicated by the short thin lines above E2 and below E4. The size of the Southern blot-detected Kpn I (K)-digested DNA fragment in igf1rlox and E3 igf1r E3 gene is indicated above the DNA fragment. The schematic diagram is not drawn to scale. Panel B. Representative Southern blot analysis of brain genomic DNA from a 2-week-old IGF1Rpre-oligo-ko mouse and a WT mouse. The sizes of DNA bands detected are indicated by two arrowheads at the left side of the image. CTX = cerebral cortex; BS = brainstem. Panel C. Representative RT-PCR analysis of mRNA isolated from CTX of a 2-week-old IGF1Roligo-ko mouse and a WT mouse. DNA ladder markers (M) were loaded on the left side of the gel, and 500 and 800 base pair (bp) bands are indicated by two arrows. Note that the bands at the bottom of both WT and KO lanes are DNA primer dimers. Panel D. A representative Western immunoblot showing the abundance of the IGF1R-β subunit in whole brain of a newborn IGF1Rpre-oligo-ko mouse (KO) and a control mouse (C).
