Figure 1.
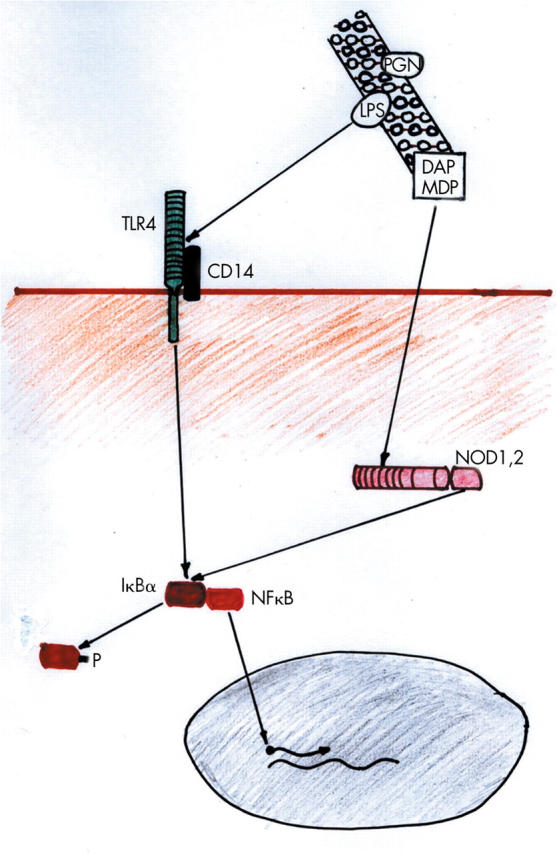
Schematic diagram of Toll-like receptor (TLR) and nucleotide binding oligomerisation domain (NOD) protein interactions with components of the bacterial cell wall and subsequent nuclear factor κB (NFκB) activation. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), diaminopimelate (DAP), and muramyl dipeptide (MDP) from the peptidoglycan (PGN) bacterial cell wall bind to TLR4, NOD1, and NOD2, respectively. Phosphorylation (P) of IκBα leads to release of NFκB which migrates to the nucleus to promote transcription of specific genes.
