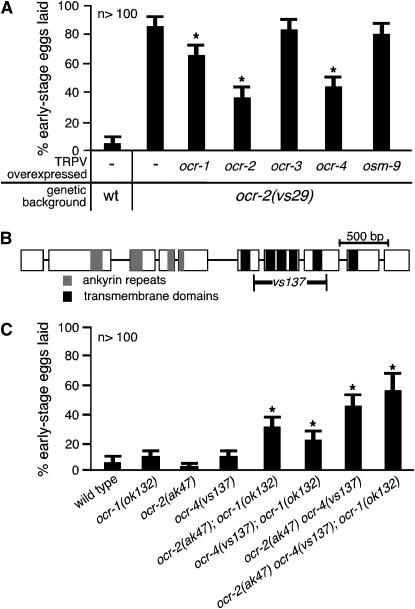
Figure 3.—
OCR-2(Y395F) likely inactivates OCR-1, -2, and -4 to cause premature egg laying. (A) Overexpression of ocr-1, ocr-2, or ocr-4 can suppress the premature egg-laying defect of ocr-2(vs29) animals. Genomic DNAs for the C. elegans TRPV genes (ocr-1, -2, -3, -4, or osm-9) were transformed into ocr-2(vs29) animals as multicopy transgenes to overexpress individual TRPV subunits. Asterisks denote significant suppression (P < 0.05) compared to ocr-2(vs29) animals lacking transgenes. wt, wild type. (B) Schematic of the ocr-4 deletion mutation: ocr-4 exons (open boxes) and introns (lines connecting boxes), sequence-coding ankyrin repeats (shaded) and transmembrane domains (solid), and the extent of the deletion (vs137) are indicated. (C) OCR-1, -2, and -4 function partially redundantly to prevent premature egg laying. Asterisks denote significant defects (P < 0.05) compared to the wild-type control (leftmost bar). No single mutant showed a significant defect, but double and triple knockouts all showed significant defects.