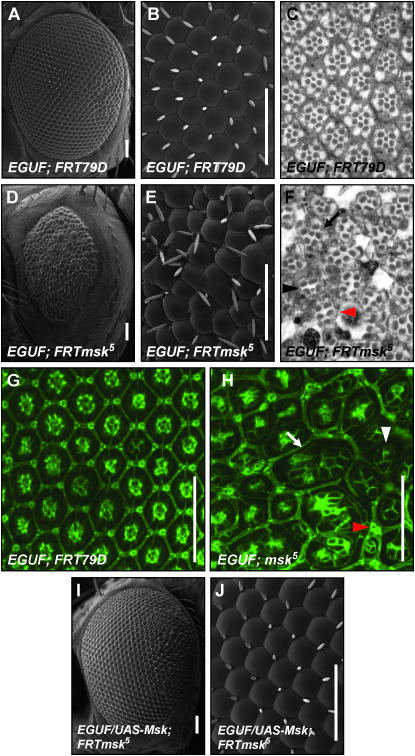
Figure 8.—
moleskin/dim-7 is required for normal eye development. An eye made entirely mutant for msk5 using the EGUF system is small and rough when compared with the control (D vs. A). At higher magnification ommatidial fusions and disruptions of the normal arrangement of bristles can be seen (compare E with B). Thin plastic sections of the EGUF; msk5 eye reveal a general disruption of normal ommatidial organization and numerous abnormal rhabdomeres (compare F with C). Some ommatidia have a normal number and arrangement of rhabdomeres (black arrow in F) while others have a decreased number of rhabdomeres per ommatidium (black arrowhead in F). Some ommatidia lack any small rhabdomeres (red arrowhead in F). This loss was verified by serial section (data not shown). At 48 hr APF the control eye has already formed the crystalline lattice seen in the adult eye (G). In the EGUF; msk5 eye, the cellular organization is clearly disrupted at 48 hr APF (H). The number of cone cells per ommatidium is often decreased to three (white arrowhead in H). Ommatidial fusions are seen where both primary and secondary pigment cells are absent (white arrow in H). Evidence of occasional bristle duplications seen by SEM in E are also apparent in the pupal disc (red arrowhead in H). The EGUF; msk5 mutant phenotype is rescued with the addition of UAS-msk (I and J). Bars, 50 μm. Genotype of EGUF; msk5 is w; ey-GAL4,UAS-flp/+; msk5, FRT79D/GMR-hid,Cl FRT79D. Genotype of EGUF control is w; ey-GAL4,UAS-flp/+; FRT79D/GMR-hid,Cl FRT79D. Genotype of EGUF/UAS-msk;FRTmsk5 is w; ey-GAL4,UAS-flp/UAS-msk; msk5,FRT79D/GMR-hid,Cl,FRT79D.