Abstract
1 The effect of calcium on the inhibition of renin secretion by biologically active angiotensin was investigated in the isolated rat kidney perfused with Krebs-Ringer saline.
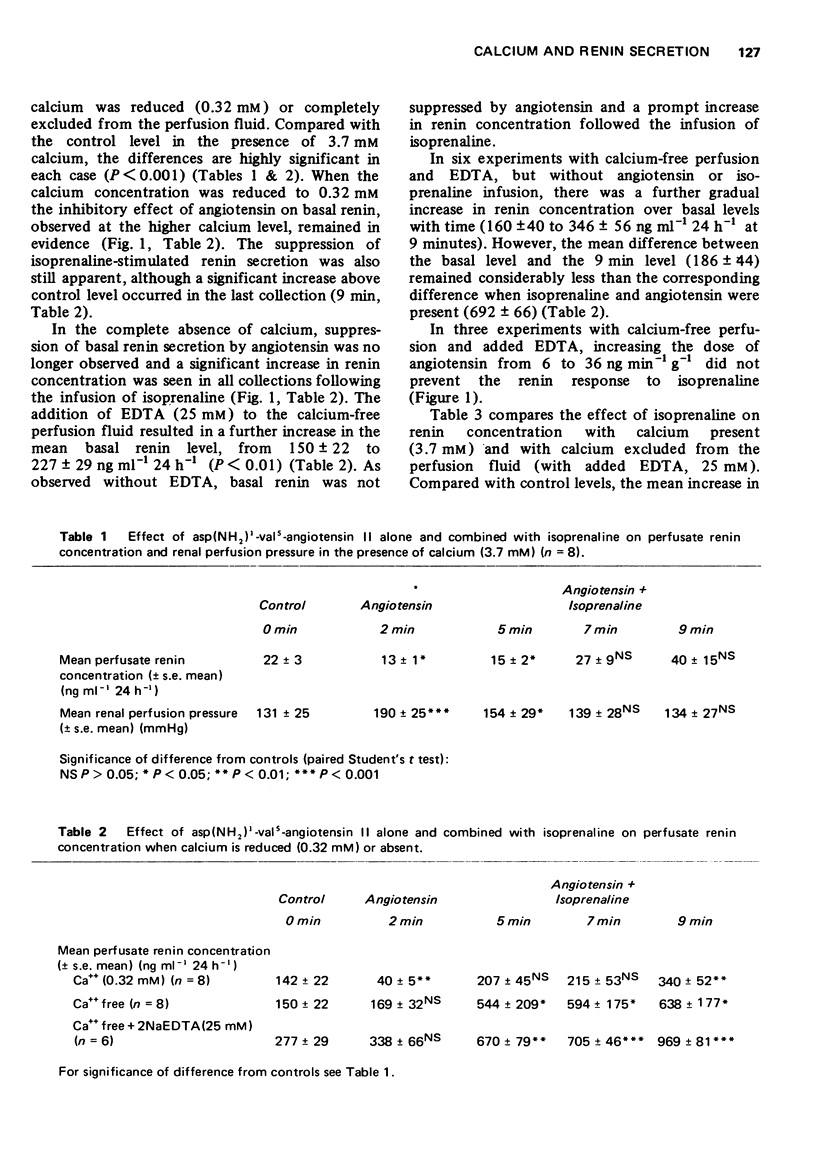
2 In the presence of calcium (3.7 mM), asp(NH2)′-angiotensin II suppressed both basal and isoprenaline-stimulated renin secretion. Renal perfusion pressure, which was increased by the infusion of angiotensin, returned to control levels when isoprenaline was added.
3 When the calcium concentration was reduced to 0.32 mM, the vasoconstriction produced by angiotensin was abolished although the inhibitory effect on renin secretion was still evident.
4 In the absence of calcium, angiotensin no longer suppressed basal renin secretion and a prompt increase in renin secretion occurred when isoprenaline was added.
5 The higher basal renin levels which were observed in calcium-free perfusions, suggest the existence of an intrarenal calcium-dependent mechanism that regulates basal renin secretion.
6 These observations indicate that the inhibitory effect of biologically active angiotensin, on basal and isoprenaline-stimulated renin secretion, is functionally related to the contractor response by its dependence on calcium. The recognition that the renin-producing cells are modified smooth muscle cells supports this association
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baudouin-Legros M., Meyer P. Effects of angiotensin, catecholamines and cyclic AMP on calcium storage in aortic microsomes. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Feb;47(2):377–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08335.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudouin M., Meyer P., Fermandjian S., Morgat J. L. Calcium release induced by interaction of angiotensin with its receptors in smooth muscle cell microsomes. Nature. 1972 Feb 11;235(5337):336–338. doi: 10.1038/235336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd G. W., Fitz A. E., Adamson A. R., Peart W. S. Radioimmunoassay determination of plasma-renin activity. Lancet. 1969 Feb 1;1(7588):213–218. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunag R. D., Page I. H., McCubbin J. W. Inhibition of renin release by vasopressin and angiotensin. Cardiovasc Res. 1967 Jan;1(1):67–73. doi: 10.1093/cvr/1.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman F. R., Weiss G. B., Weinberg M. N., Pomarantz S. D. Effects of added or substituted potassium ion on 45 Ca movements in rabbit aortic smooth muscle. Circ Res. 1972 Nov;31(5):672–681. doi: 10.1161/01.res.31.5.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keatinge W. R. Mechanical response with reversed electrical response to noradrenaline by Ca-deprived arterial smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(1):21–34. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner S. L. Improved assay methods for renin "concentration" and "activity" in human plasma. Methods using selective denaturation of renin substrate. Circ Res. 1967 Apr;20(4):391–402. doi: 10.1161/01.res.20.4.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. P., Somlyo A. V. Vascular smooth muscle. I. Normal structure, pathology, biochemistry, and biophysics. Pharmacol Rev. 1968 Dec;20(4):197–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan L. J., Briggs A. H. Effects of manganese on the response of aortic strips to angiotensin and norepinephrine contractions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Jun;161(2):205–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Breemen C., Farinas B. R., Gerba P., McNaughton E. D. Excitation-contraction coupling in rabbit aorta studied by the lanthanum method for measuring cellular calcium influx. Circ Res. 1972 Jan;30(1):44–54. doi: 10.1161/01.res.30.1.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J. Inhibition of renin release in the dog by vasopressin and vasotocin. Circ Res. 1968 Nov;23(5):605–609. doi: 10.1161/01.res.23.5.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandongen R., Peart W. S., Boyd G. W. Andrenergic stimulation of renin secretion in the isolated perfused rat kidney. Circ Res. 1973 Feb;32(2):290–296. doi: 10.1161/01.res.32.2.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


