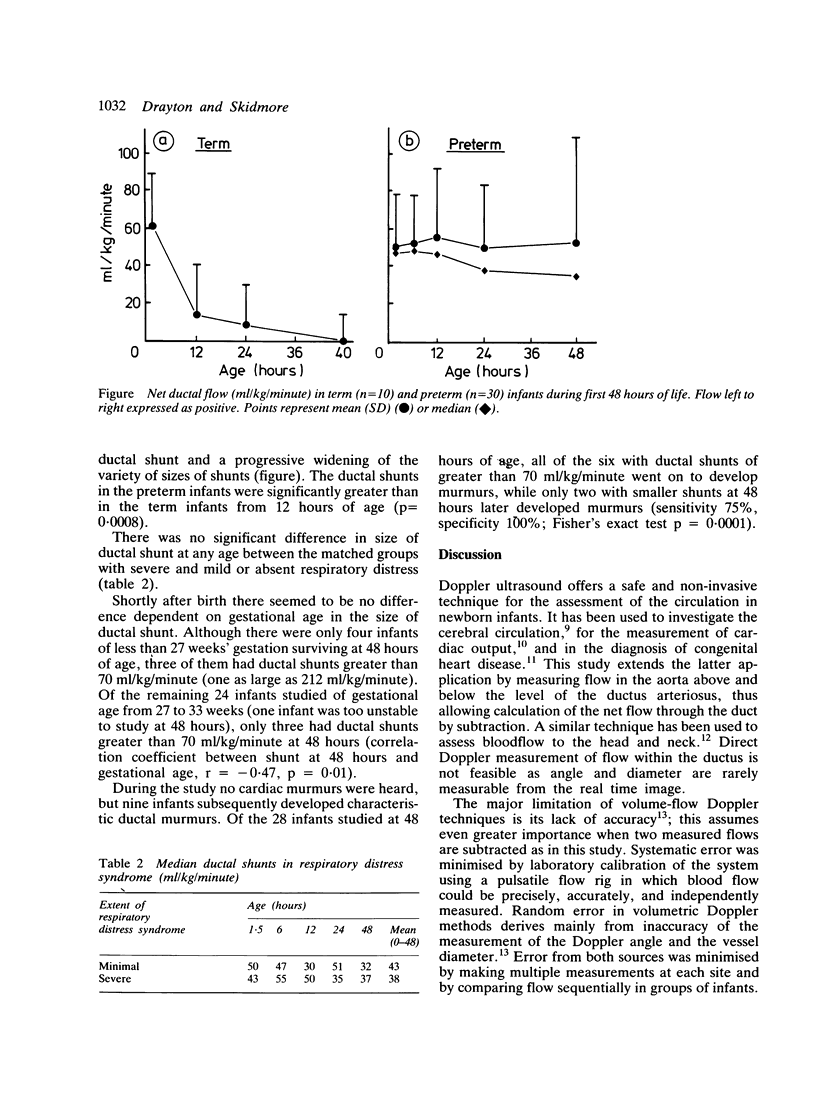
Abstract
A volumetric Doppler technique was used to measure net ductus arteriosus shunt during the first 48 hours of life in 30 infants of less than 33 weeks' gestation, and in 10 full term infants. In the full term infants a left to right shunt of 62 ml/kg/minute (95% confidence limits 43-82) shortly after birth decreased rapidly over the first 12 hours and was not measurable by 48 hours. The preterm infants had smaller left to right shunts shortly after birth--49 ml/kg/minute (95% confidence limits 38-59). There was no obvious subsequent change in the mean shunt, although by 48 hours there was greater variation in the size of the shunt. The respiratory distress syndrome did not affect the size of the ductal shunt, but the shorter the gestation period the larger the shunt by 48 hours. A ductal flow of greater than 70 ml/kg/minute at 48 hours of age predicted the subsequent development of a ductal murmur with 75% sensitivity and 100% specificity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alverson D. C., Eldridge M., Dillon T., Yabek S. M., Berman W., Jr Noninvasive pulsed Doppler determination of cardiac output in neonates and children. J Pediatr. 1982 Jul;101(1):46–50. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80178-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayton M. R., Skidmore R. Doppler ultrasound in the neonate. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1986 Oct;12(10):761–772. doi: 10.1016/0301-5629(86)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayton M. R., Skidmore R. Vasoactivity of the major intracranial arteries in newborn infants. Arch Dis Child. 1987 Mar;62(3):236–240. doi: 10.1136/adc.62.3.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentile R., Stevenson G., Dooley T., Franklin D., Kawabori I., Pearlman A. Pulsed Doppler echocardiographic determination of time of ductal closure in normal newborn infants. J Pediatr. 1981 Mar;98(3):443–448. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80719-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill R. W. Measurement of blood flow by ultrasound: accuracy and sources of error. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1985 Jul-Aug;11(4):625–641. doi: 10.1016/0301-5629(85)90035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitterman J. A., Edmunds L. H., Jr, Gregory G. A., Heymann M. A., Tooley W. H., Rudolph A. M. Patent ducts arteriosus in premature infants. Incidence, relation to pulmonary disease and management. N Engl J Med. 1972 Sep 7;287(10):473–477. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197209072871001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSS A. J., EMMANOUILIDES G., DUFFIE E. R., Jr Closure of the ductus arteriosus in the newborn infant. Pediatrics. 1963 Jul;32:25–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath R. L., McGuinness G. A., Way G. L., Wolfe R. R., Nora J. J., Simmons M. A. The silent ductus arteriosus. J Pediatr. 1978 Jul;93(1):110–113. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80617-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PREC K. J., CASSELS D. E. Dye dilution curves and cardiac output in newborn infants. Circulation. 1955 May;11(5):789–798. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.11.5.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUDOLPH A. M., DRORBAUGH J. E., AULD P. A., RUDOLPH A. J., NADAS A. S., SMITH C. A., HUBBELL J. P. Studies on the circulation in the neonatal period. The circulation in the respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatrics. 1961 Apr;27:551–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberton N. R., Dahlenburg G. W. Ductus arteriosus shunts in the respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatr Res. 1969 Mar;3(2):149–159. doi: 10.1203/00006450-196903000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serwer G. A., Armstrong B. E., Anderson P. A. Continuous wave Doppler ultrasonographic quantitation of patent ductus arteriosus flow. J Pediatr. 1982 Feb;100(2):297–299. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80658-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serwer G. A., Armstrong B. E., Anderson P. A. Nonivasive detection of retrograde descending aortic flow in infants using continuous wave doppler ultrasonography. Implications for diagnosis of aortic run-off lesions. J Pediatr. 1980 Sep;97(3):394–400. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spach M. S., Serwer G. A., Anderson P. A., Canent R. V., Jr, Levin A. R. Pulsatile aortopulmonary pressure-flow dynamics of patent ductus arteriosus in patients with various hemodynamic states. Circulation. 1980 Jan;61(1):110–122. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.61.1.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thibeault D. W., Emmanouilides G. C., Nelson R. J., Lachman R. S., Rosengart R. M., Oh W. Patent ductus arteriosus complicating the respiratory distress syndrome in preterm infants. J Pediatr. 1975 Jan;86(1):120–126. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80722-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON R. R. Post-mortem observations on contraction of the human ductus arteriosus. Br Med J. 1958 Apr 5;1(5074):810–812. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5074.810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


