Figure 1.
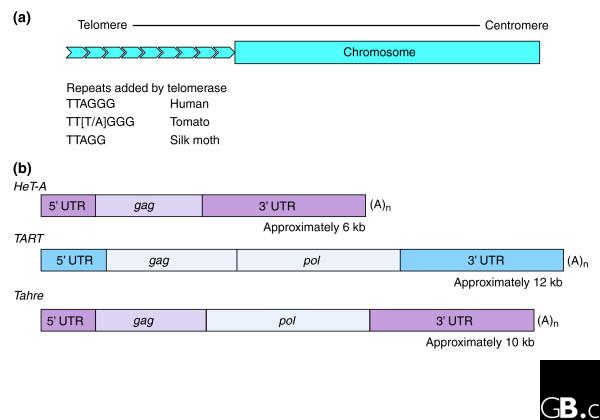
Comparison of telomeres maintained by telomerase with those maintained by the transposition of retrotransposons. (a) Eukaryotic telomeres are composed of long chains of head-to-tail repeats. In many organisms other than Drosophila, the repeats are short simple sequences of around 6 bp and telomeres are maintained by addition of repeats to the ends of the telomeres by the enzyme telomerase. (b) In Drosophila, each repeat is a non-LTR retrotransposon, of which there are three different types, HeT-A, TART, and Tahre, ranging from 6 kb to 12 kb in length. These elements transpose as poly(A)+ RNA and are reverse transcribed onto the end of the chromosome to extend the telomere. The gag and pol are characteristic retroviral genes encoding structural proteins and viral enzymes, respectively. The colors of the segments indicate that HeT-A and Tahre share sequences of 5' UTR, 3' UTR, and gag while TART and Tahre have similar pol sequences but have very different 5' UTR, 3' UTR and gag sequences.
