Figure 2.
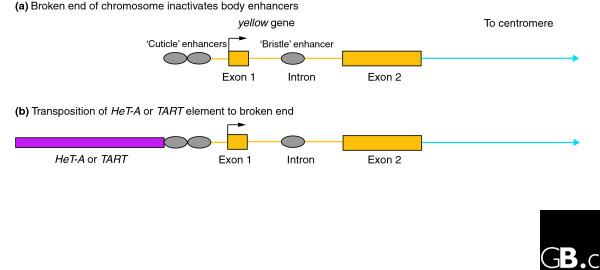
Assay to measure the frequency of transposition onto a chromosome end. Expression of the yellow gene (which controls normal pigmentation) is controlled in different body tissues by enhancers located in different regions of the gene. (a) A break at the end of the chromosome inactivates upstream enhancers that direct expression of the yellow gene in the cuticle, producing flies with a yellow (mutant) body but still producing normal pigmentation in the bristles, as directed from the intronic enhancer. (b) Transposition of HeT-A or TART to the broken end reactivates the upstream enhancer for expression of yellow+ in the aristae (the terminal segments of the antenna), and these structures are pigmented normally.
