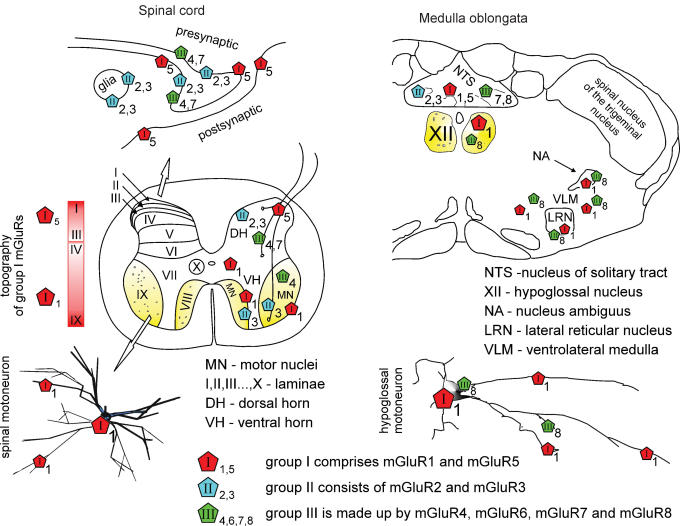
Figure 1. Topography of mGluRs in the spinal cord and brainstem.
Left, top scheme shows that the majority of mGluR immunoreactivity is found on the perisynaptic and extrasynaptic plasma membrane of neurons, and partly on glia. Middle, schematic section of the adult rat spinal cord indicates that mGluR5s are densely expressed in laminae I–III of the dorsal horn (DH) with gradual decrease in deeper laminae. About half of vesicle-containing profiles stained for mGluR5 are also positively stained for GABA (Jia et al. 1999). mGluR1s are mostly distributed throughout laminae III–X (Berthele et al. 1999; Alvarez et al. 2000) with patchy immunoreactivity of varying intensity in somata and dendrites of spinal motor nuclei (MN) including motoneurons and interneurons (see inset marked by open arrow) of the ventral horn (VH), and in presynaptic axon terminals (Alvarez et al. 1997, 2000). Group II and III are scattered throughout the spinal cord with predominance in the DH (Berthele et al. 1999) and even some glial labelling (Ohishi et al. 1995; Jia et al. 1999; Azkue et al. 2000, 2001). In addition, group II mGluR3 mRNA is expressed in the small cells surrounding motoneurons, while group III mGluR4 mRNA is present in the spinal motoneurons (Berthele et al. 1999). Right, in the medulla oblongata group I (mGluR1a/5), group II (mGluR2/3) and group III (mGluR7/8) mGluRs (Hay et al. 1999; Pamidimukkala et al. 2002) show different distribution throughout subnuclei of NTS and of the ventrolateral medulla. Only mGluR1 and mGluR8 subtypes are expressed by hypoglossal motoneurons (XII; Hay et al. 1999; Pamidimukkala et al. 2002).