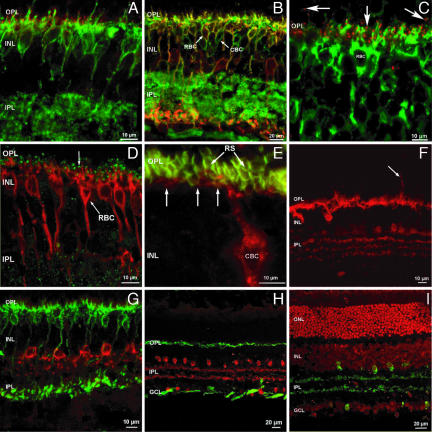
Fig. 2.
Synaptic organization of the inner retina in the absence of cones. (A) The glutamatergic receptor mGluR6 is clustered selectively at puncta (red) in the OPL, on the dendritic tips of ON bipolar cells, labeled by G0α antibodies (green). (B) G0α antibody labels the whole population of ON bipolar cells (green signal), whereas PKCα labels rod bipolar cells only (RBC; red). Rod bipolar neurons are therefore double-labeled by both antibodies and appear yellow. Green cells are ON cone bipolar cells (indicated as CBC). (C) mGluR6 receptors are labeled as red puncta located at the dendritic tips of rod bipolar cells, labeled green by PKCα antibodies. In addition, clusters of mGluR6 are visible in the OPL, but not in association with rod biolar cell dendrites. These clusters are likely to be associated to the dendrites of ON cone bipolar cells. (D) Rod bipolar cells (RBC), labeled by PKCα (red), are postsynaptic to photoreceptors in the OPL at ribbon synapses (indicated by R), as indicated by antibodies against kinesin, a synaptic ribbon marker (green). (E) High magnification of one type of cone bipolar cell (CBC), labeled with NK3-R antibody (red). Rod spherules (RS) are labeled with anti-PSD95 antibody (green). Few dendrites of cone bipolar cells reach the basal aspect of some spherules (arrows); however, many spherules do not appear apposed to CBC dendrites, although these belong to one of the most abundant types of retinal cone bipolar cell. (F) Calbindin staining (red) of the Crxp-Nrl/WT retina shows a normal distribution of intensely labeled horizontal cells and weakly fluorescent amacrine cells with their processes in the IPL. Occasionally, horizontal cell sprouts are observed (arrow). (G) AII amacrine cells (the most abundant population of mammalian amacrines) are specifically stained with DB3 antibodies (red). They exhibit a typical, bistratified morphology. The innermost dendrites terminate in apposition to the axonal endings of rod bipolar cells, stained green by PKCα antibodies. (H) Cholinergic amacrine cells are stained in the transgenic retina by ChAT antibodies (red). The cells form two mirror symmetric populations of neurons. Axonal complexes of horizontal cells are labeled with neurofilament antibodies (green). Axonal fascicles of ganglion cells are also intensely stained in the optic fiber layer. (I) Ethidium bromide nuclear staining (red) and ChAT immunostaining (green) demonstrate the normal layering and lamination of the transgenic retina. OS, outer segments; ONL, outer nuclear layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer.