Figure 1.
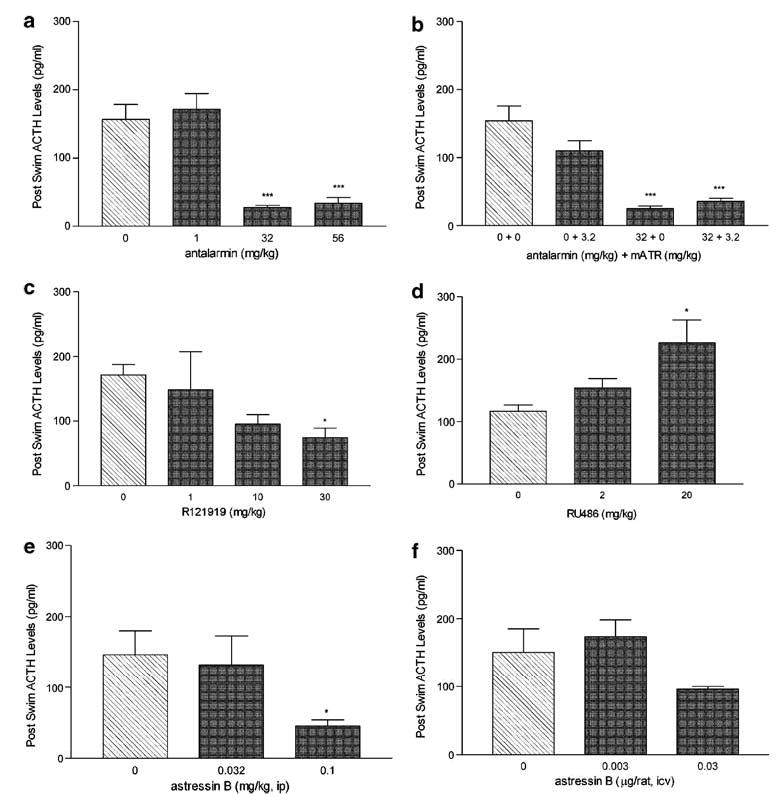
The effects of CRF antagonists, GR antagonists and methylatropine challenge on postswim ACTH levels. Each panel represents the dose-dependent effects of each drug (dark bars) vs vehicle (hatched bar) treatment on ACTH at the time of sinking or at the end of the 2 h swim (n = 6 rats per dose of drug) expressed as mean pg/mL (±SEM); (a), antalarmin; (b) antalarmin + methylatropine nitrate (mATR); (c), R121919; (d), RU486; (e), astressin B—ip; and (f) astressin B—icv. Blood was collected at time of sinking or at the end of the two hour swim. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001 vs 0 mg/kg treatment.
