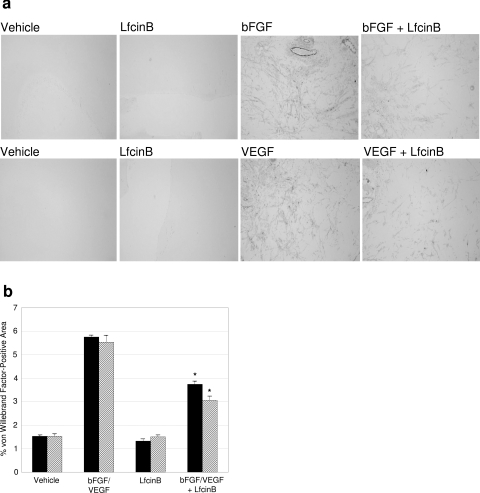
Figure 1.
LfcinB inhibits bFGF- and VEGF165-induced angiogenesis. Matrigel containing distilled water (vehicle), LfcinB alone (200 μg/ml), bFGF (1 μg/ml), VEGF165 (5 μg/ml) alone, or LfcinB (200 μg/ml) in combination with bFGF (1 μg/ml) or VEGF165 (5 μg/ml) was implanted in mice by subcutaneous injection. After 6 days, mice were sacrificed, Matrigel plugs were surgically excised and sectioned, and blood vessel formation was visualized by staining with rabbit antibody that recognizes murine von Willebrand factor. a: Representative sections of Matrigel plugs containing vehicle, LfcinB, or bFGF/VEGF165 alone or in combination with LfcinB. b: Measurement of mean capillary area in Matrigel plugs. The area of individual Matrigel plugs sections that stained positive for von Willebrand factor relative to the unstained area was determined by computer analysis. Each bar represents mean percentage of von Willebrand factor-positive area ± SEM (n = 8). Statistical significance was determined by the Tukey-Kramer multiple comparisons test; *P < 0.001. Original magnifications, ×20.