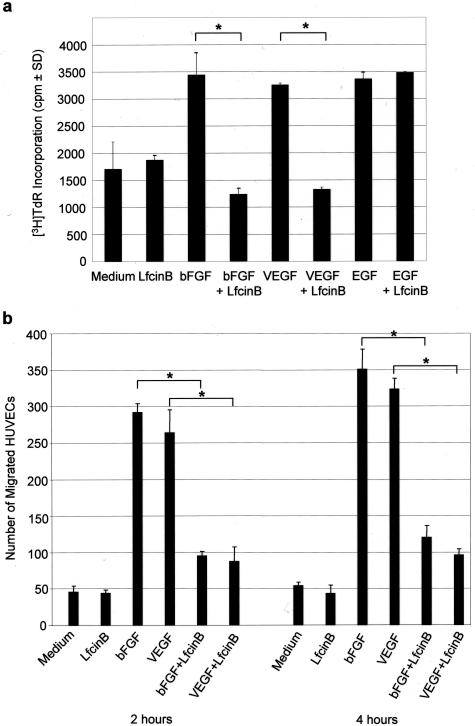
Figure 3.
LfcinB inhibits bFGF- and VEGF165-induced HUVEC proliferation and migration. a: HUVECs (4 × 103 cells/well) were cultured for 24 hours in the presence of medium, LfcinB (200 μg/ml), bFGF (10 ng/ml), VEGF165 (100 ng/ml), or nonheparin-binding EGF (20 ng/ml) alone or with bFGF (10 ng/ml), VEGF165 (100 ng/ml), or EGF (20 ng/ml) in combination with LfcinB (200 μg/ml). DNA synthesis was measured by [3H]TdR incorporation. Data are shown as mean cpm ± SD of quadruplicate determinations. Statistical significance was determined by the Tukey-Kramer multiple comparisons test; *P < 0.001. b: HUVECs (5 × 105 cells) were added to the upper chamber. Medium, LfcinB (200 μg/ml), bFGF (10 ng/ml), or VEGF165 (100 ng/ml) alone or bFGF (10 ng/ml) or VEGF165 (100 ng/ml) in combination with LfcinB (200 μg/ml) was added to the bottom chamber. After 2- and 4-hour incubations, filters were fixed and stained with hematoxylin, and HUVECs that had migrated across the filter were enumerated by light microscopy. Data are shown as mean number of migrated HUVECs ± SD of triplicate determinations. Statistical significance was determined by the Tukey-Kramer multiple comparisons test; *P < 0.001.